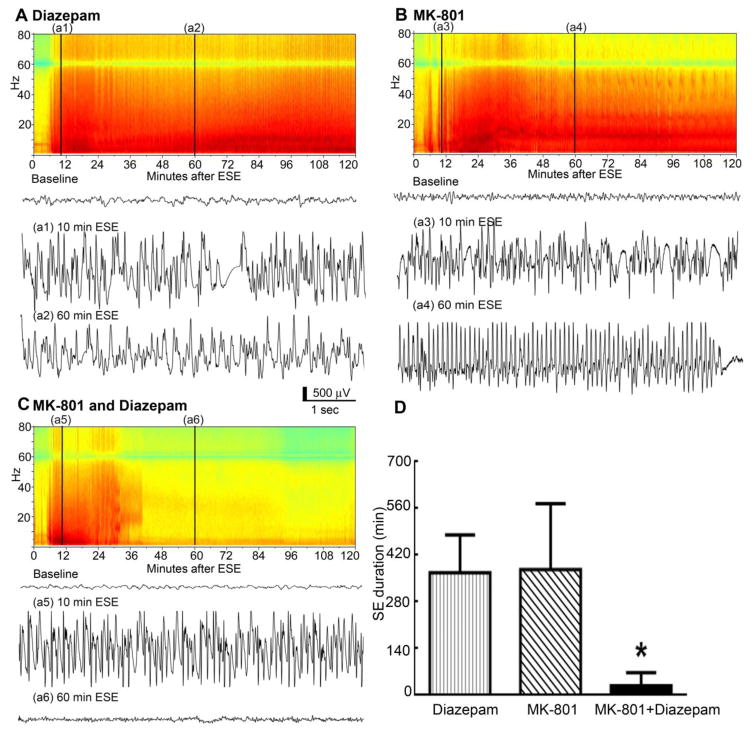
Figure 5. The combination of diazepam and MK-801 terminated benzodiazepine-refractory SE.
The EEG power spectrum during the first 120 min of ESE in the representative animals treated with (A) diazepam alone (10 mg/kg), (B) MK-801 alone (2 mg/kg) or (C) a combination of diazepam and MK-801 at 10 min ESE triggered by pilocarpine. In the spectrum, increasing power is represented by the change in color from blue to red. The low power at 60 Hz is due to the application of a notch filter to reduce the 60-cycle artifact. Conventional EEG traces from the same animal at baseline and at 10, 60, and 120 min ESE are shown below the power display. The combination of MK-801 and diazepam led to the rapid termination of seizures, after which the EEG returned to the baseline level, whereas seizures continued despite the treatments when these drugs were administered alone. (D) Mean ± SEM of seizure duration from the onset of continuous seizure activity (N=5 each for diazepam or MK-801 alone and N=6 for the diazepam and MK-801 combination treatment, * p<0.05, ANOVA with Dunn’s post hoc multiple comparison test).