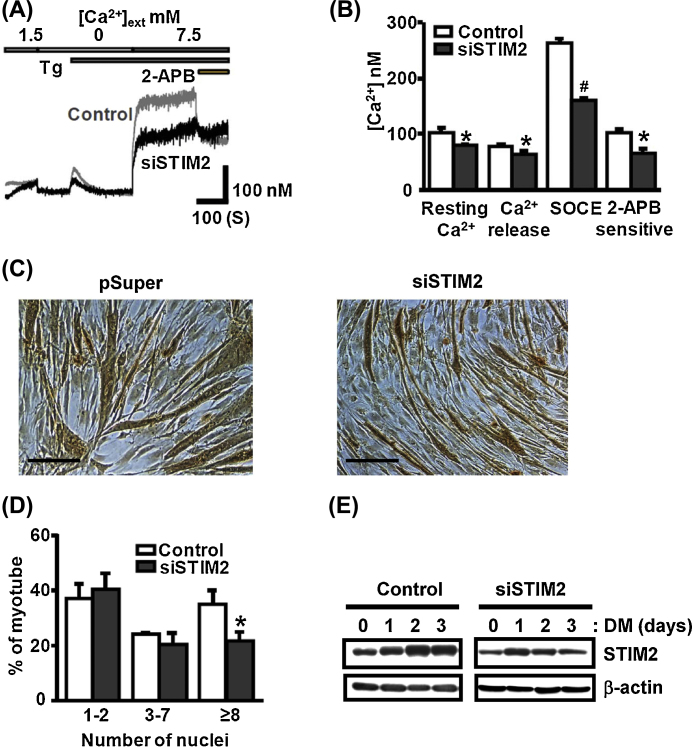
Fig. 3.
Knockdown (KD) of STIM2 reduces SOCE activity and impairs C2C12 myoblast differentiation. (A) Representative traces of [Ca2+]i measured at differentiation Day 3 (DM3) from control or STIM2-KD (siSTIM2) myotubes. (B) Summary bar graphs represent the changes in resting [Ca2+]i, SR Ca2+ release, SOCE activity, and 2-APB-sensitive SOCE component by knockdown of STIM2 (n = 3; *p < 0.05, #p < 0.01). (C) Representative images of MyHC+ cells taken from control and STIM2-KD myotubes at DM3. Shown are representative images from three independent experiments. Scale bars = 100 μm. (D) Quantification of nuclei number in MyHC+ cells at DM3. The percentage of MyHC+ myotubes with eight or more nuclei was 61.85 ± 16.8% of control (n = 3, *p < 0.05). (E) The decreased STIM2 protein expression level was maintained during 3 days of differentiation of STIM2-KD myoblasts. A representative immunoblotting is depicted from two independent experiments.
KD, knockdown; SOCE, store-operated Ca2+ entry; SR, sarcoplasmic reticulum; STIM2, stromal interaction molecule 2.