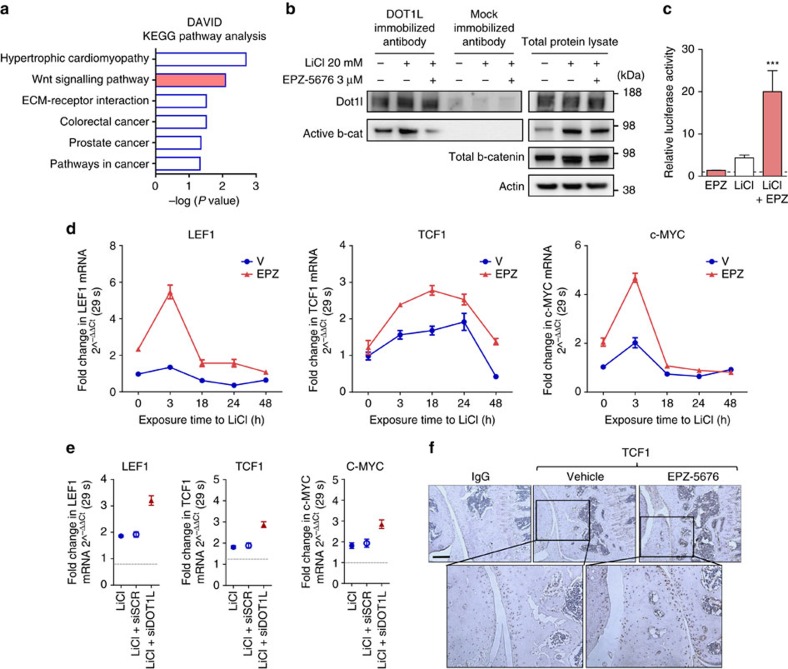
Figure 2. DOT1L negatively regulates Wnt signalling in articular cartilage.
(a) KEGG pathway enrichment analysis of microarray data obtained from human articular chondrocytes treated with EPZ-5676 or vehicle. Nominal P values by EASE modified Fisher Exact test using the DAVID analysis tool (see Methods section) are shown. n=5 independent patient-derived cell cultures. (b) Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) using an anti-DOT1L antibody showing interaction between DOT1L and β-catenin in human articular chondrocytes, that is increased upon Wnt activation by LiCl and disrupted upon DOT1L inhibition. The image is representative of three experiments. (c) TOP/FOP reporter assay in human articular chondrocytes after Wnt stimulation by LiCl and DOT1L inhibition by EPZ. Activity is compared to untreated cells (dotted line). n=3 biologically independent experiments. ***P<0.001 by one-way ANOVA. (d,e) LEF1, TCF1 and c-MYC expression measured by quantitative PCR in chondrocytes treated with EPZ-5676 and LiCl (d) or in LiCl-treated chondrocytes transfected with siRNA directed against DOT1L or scrambled siRNA (siDOT1L or siSCR, respectively) (e). Data are from one experiment with three technical replicates. (f) Immunohistochemistry demonstrating increased TCF1 levels in the articular cartilage of C57/Bl6 wild-type mice after injection of EPZ-5676. The images are representative of three different animals. Scale bar, 200 μm.