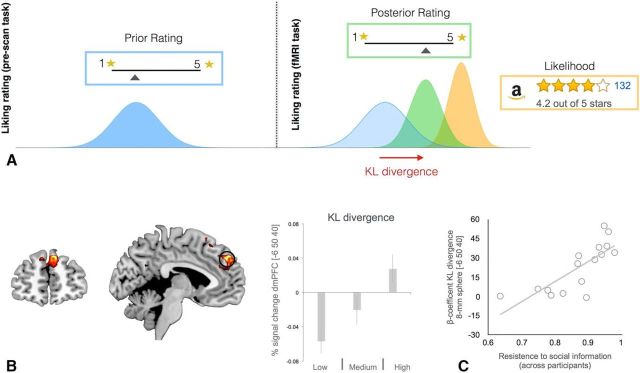
Figure 4.
A, Schematic representation of the Bayesian update of liking ratings in response to social information communicated through reviews. The KL divergence parameter indexes the impact of the reviews in shifting the liking rate from the first rating (made in the absence of review information) and the second rating (performed by the participants after seeing the Amazon reviews). B, BOLD signal in dmPFC (peak = −6,50,40) correlates with increase in KL divergence (z = 3.66, p < 0.05, FWE small volume corrected). Percentage signal change for three levels (low, medium, and high) of KL divergence is shown. The histogram plot is not used for statistical inference (which was performed in the SPM framework); it is shown solely to illustrate the dynamic of the BOLD signal. Error bars indicate SEM. C, Between-subject correlation between activity in dmPFC (8 mm ROI centered at −6,50,40) and the degree of resistance to social information (r = 0.77, p < 0.0005). This analysis shows that people who are less influenced by the opinion expressed by others in the reviews have overall more activity in this area.