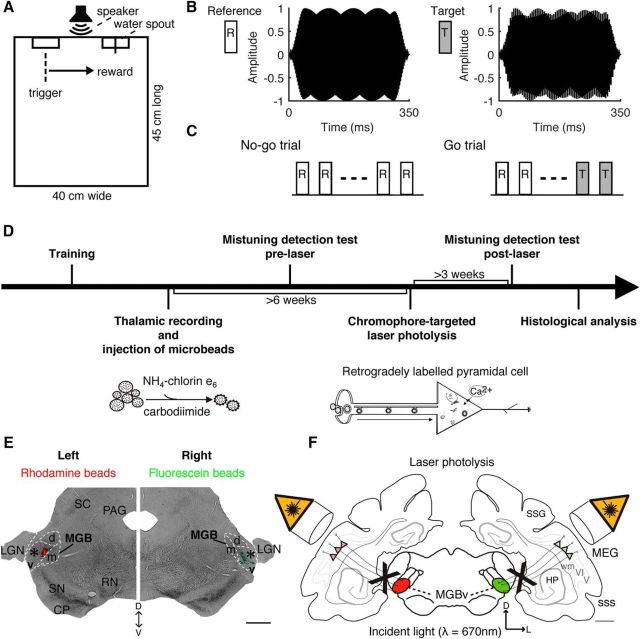
Figure 3.
Experimental design. A, The behavioral testing chamber contained two water spouts, labeled as trigger (left) and reward (right) spouts. In between, a loudspeaker was mounted at a height of 20 cm. B, Spectral envelopes of the reference HCT (F0, 400 Hz; 16 harmonics) and the target tone (MCT, 192 Hz shift in the fourth harmonic). Stimuli were 350 ms long and had a 25 ms Hanning ramp at the onset and offset. C, No-go trials comprised three to seven reference tones, whereas go trials comprised two to six reference tones followed by two target tones. D, After initial behavioral training, the lesion group received injections, guided by electrophysiological recordings, of fluorescent microbeads conjugated with chlorin e6 in the MGBv. Sham operations were performed in the controls. After measuring mistuning detection, A1 was exposed bilaterally to near-infrared laser light to induce apoptosis of corticothalamic projection neurons. Three weeks later, mistuning detection was tested again. Finally, brains underwent histological analysis to quantify the corticothalamic lesions. E, Coronal section of one animal at the level of the auditory thalamus, indicating the injection sites of rhodamine (red) and fluorescein (green) microbeads in the left and right MGBv, respectively (asterisks). F, Summary of experimental design for lesioning auditory corticothalamic neurons. V/VI, cortical layers V and VI; PAG, periaqueductal gray; RN, red nucleus; SC, superior colliculus; SN, substantia nigra; sss, suprasylvian sulcus; wm, white matter. Other abbreviations are as in Figure 1 legend. Scale bars, 1 mm.