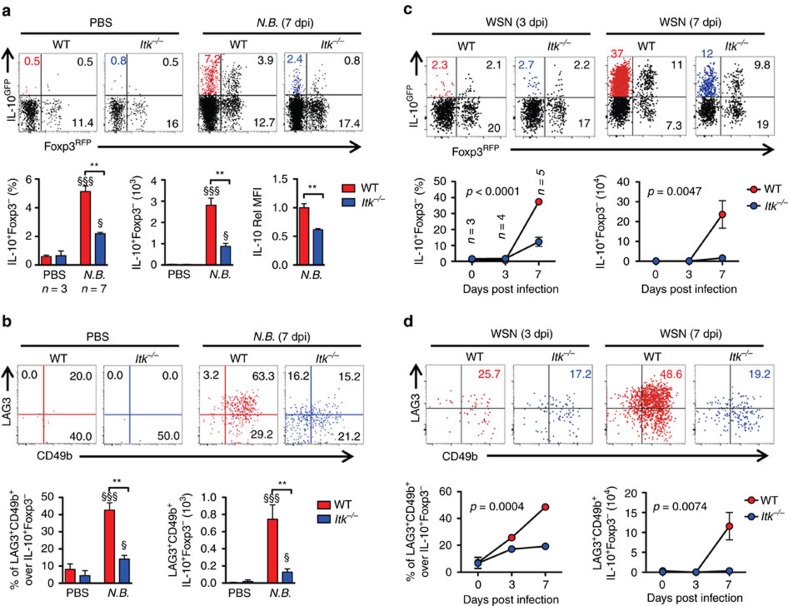
Figure 2. ITK is required for parasitic/viral infection-induced Tr1 cell development in vivo.
(a,b) ITK is required for Tr1 cell development during parasitic infection: WT and Itk−/− mice were infected with 500 L3 N. brasiliensis (N.B.) and lungs analyzed 7 days post infection (d.p.i.). (a) Representative FACS plots showing IL-10GFP and Foxp3RFP expression by pulmonary CD4+ T cells and summary of IL-10+Foxp3− T cell percentage, number and IL-10 expression levels (WT average level set as 1). (b) Representative FACS plots showing the LAG3 and CD49b expression by IL-10GFP+ Foxp3RFP− CD4+ T cells, summary of LAG3+CD49b+ IL-10+Foxp3−CD4+ Tr1 cell percentage and number from samples shown in a. §P≤0.05, §§P≤0.01, §§§P≤0.001, compared with PBS-treated group; *P≤0.05, **P≤0.01, ***P≤0.001, comparing groups connected, by non-parametric Mann-Whitney test. (c,d) ITK is required for Tr1 cell development during viral infection: WT and Itk−/− mice were infected with 104 PFU Influenza A/WSN/1933 (WSN) and lungs analyzed 3 and 7 d.p.i. (c) Representative FACS plots showing IL-10GFP and Foxp3RFP expression by pulmonary CD4+ T cells and summary of IL-10+Foxp3− T cell percentage, number and IL-10 expression levels (WT average level set as 1). (d) Representative FACS plots showing the LAG3/CD49b expression by IL-10GFP+ Foxp3RFP− CD4+ T cells, summary of LAG3+CD49b+ IL-10+Foxp3−CD4+ Tr1 cell percentage and number from samples shown in c. P values on plots were calculated by two-way ANOVA. Data were pooled from three experiments, ‘n’ indicates number of replicates in each group/point. Data presented as mean±s.e.m.