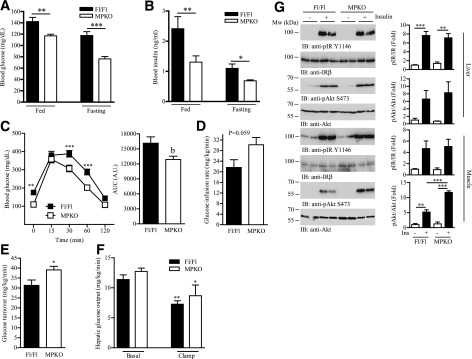
Figure 3.
Ablation of PIKE gene in the skeletal muscle alleviates diet-induced insulin resistance. A: Blood glucose concentration in mice that have been fed with HFD for 14 weeks (**P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001, Student t test; n = 6). B: Circulating insulin concentration in mice that have been fed with HFD for 14 weeks (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, Student t test; n = 6). C: Glucose tolerance test in mice that have been fed with HFD for 14 weeks (**P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001, two-way ANOVA; bP < 0.01, Student t test; n = 12). D: Glucose infusion rate in mice that have been fed with HFD for 14 weeks during the hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp experiment (n = 6, Student t test). E: Glucose turnover rate in mice that have been fed with HFD for 14 weeks during the hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp experiment (*P < 0.05, Student t test; n = 6). F: Hepatic glucose production in mice that have been fed with HFD for 14 weeks during the hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp experiment (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, one-way ANOVA vs. the same genotype; n = 6). G: Representative result of immunoblotting (IB) analysis in hind limb skeletal muscle (mixed fiber type) and liver of female mice that have been fed with HFD for 14 weeks. Quantification of the immunoblotting analysis is also shown in right panel (**P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001, one-way ANOVA; n = 3). A.U., arbitrary units; AUC, area under the curve; pAkt, phosphorylated Akt; pIR, phosphorylated insulin receptor.