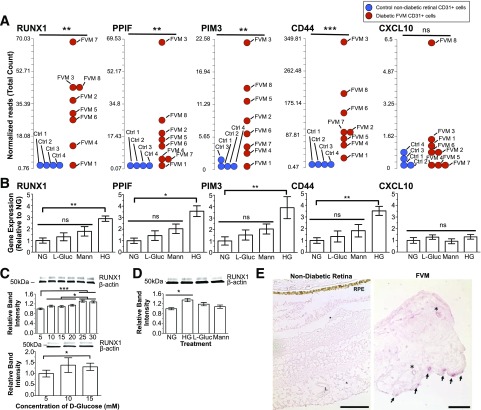
Figure 2.
Effect of elevated glucose on HRMEC gene expression. A: Results of FVM RNA-sequencing (reads per kilobase of transcript per million mapped reads) show increased expression of RUNX1, PPIF, PIM3, and CD44 in ECs from patients with PDR compared with patients without diabetes. CXCL10 did not exhibit increased expression in FVMs (ncontrols = 4; nPDR-FVM = 8). B: Corresponding gene expression of RUNX1, PPIF, PIM3, CD44, and CXCL10 measured by qRT-PCR (HG, high d-glucose [30 mmol/L]; NG, normal d-glucose [5 mmol/L]). Each candidate gene had a marked increase in response to d-glucose but no statistically significant changes in response to osmotic controls (L-glucose or mannitol). CXCL10 is not glucose responsive, consistent with RNA-sequencing (n = 3; the experiment was performed in triplicate). C: Increasing d-glucose led to a dose-dependent increase of RUNX1 protein expression in HRMECs (top) and HUVECs (bottom) as determined by Western blot (n = 3; experiment performed in triplicate). D: The increase in RUNX1 protein in HRMECs induced by 30 mmol/L d-glucose was independent of osmotic forces (n = 3; experiment performed in triplicate). E: Normal retinal vessels showed no staining of RUNX1 (L, vessel lumen; RPE, retinal pigment epithelium) (left panel). Scale bars = 100 μm. A subset of vessels in FVM stained positively for RUNX1 (arrows). Asterisks denote nonstaining vessels (left). Scale bar = 50 μm. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.