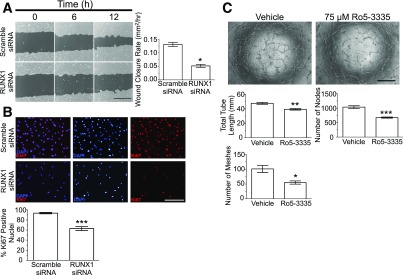
Figure 3.
Role of RUNX1 in EC function. A: Scratch-wound assay using HRMECs at 0 (left column), 6 (middle column), and 12 h (right column) with scramble siRNA (top) and RUNX1 siRNA (bottom) treatment. Dark gray regions denote wound areas. Scale bar = 400 μm. Quantification of wound closure rates shows that knockdown of RUNX1 effectively inhibits wound closure (n = 10; experiment performed in duplicate). B: Ki67 staining 48 h posttransfection demonstrates significant reduction in cell number and proliferative capacity of RUNX1 siRNA-treated cells compared with cells treated with scramble siRNA. Scale bar = 200 μm. Quantification of percentage of DAPI-positive nuclei colocalized with Ki67 stain (n = 6; experiment performed in duplicate). C: HRMECs treated with Ro5–3335 RUNX1 inhibitor overnight exhibited reduced tube-forming capacity compared with vehicle-treated cells at 6 h after plating. There was statistically significant reduction in tube length, meshes, and nodes. Scale bar = 500 μm. n = 4; experiment performed in duplicate. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.