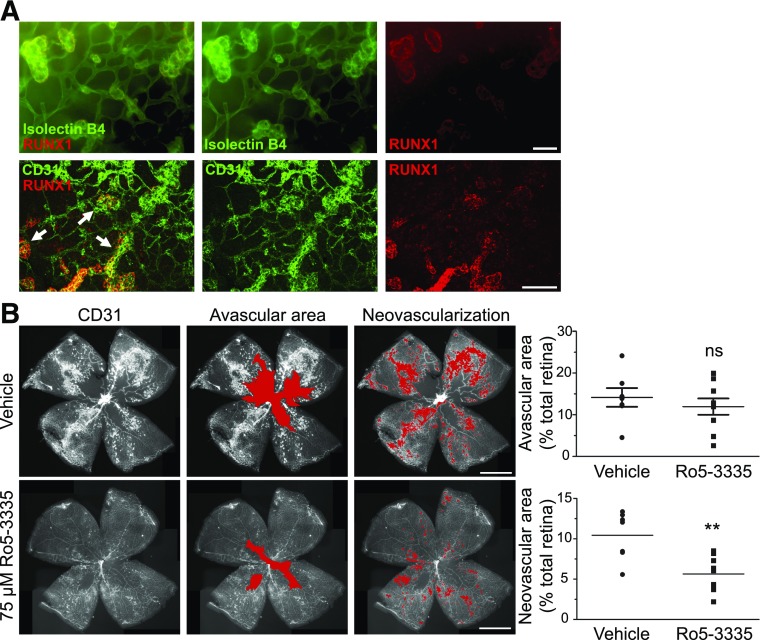
Figure 4.
RUNX1 inhibition reduces neovascularization in the OIR model. A: Retina of P17 C57BL/6J mice with OIR costained for RUNX1 and vessels (IB4 or CD31) showing positive RUNX1 staining conforming to neovascular tufts (arrows) and not to normal underlying vasculature. Scale bars = 50 μm. B: Retinal flat mounts of P17 C57BL/6J mice following OIR induction and intravitreal injection of 75 μmol/L Ro5–3335 or vehicle at P13 and P15 (red overlay identifies the avascular area and neovascularization, respectively). Scale bars = 1 mm. There was a nonsignificant downward trend in avascular area but a significant reduction in neovascularization in the treated group compared with vehicle-treated group (nvehicle = 7; nRo5–3335 = 9). Experiment performed in triplicate. **P < 0.01.