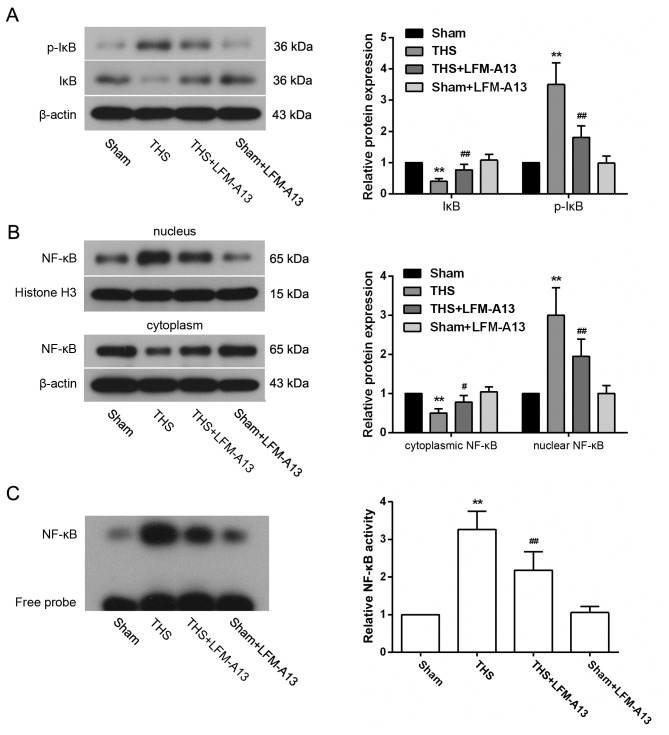
Figure 5.
Effects of Bruton's tyrosine kinase on pulmonary NF-κB activity in THS rats. Protein expression levels of (A) p-IκB and IκB, and (B) nuclear and cytoplasmic NF-κB were detected by western blotting and densitometric analysis. (C) Binding activity of NF-κB was analyzed by electrophoretic mobility shift assay (n=5 rats/group). Typical bands are shown. Data are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation, **P<0.01 vs. Sham group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs. untreated THS group. IκB, inhibitor of NF-κB; LFM-A13, a Bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibitor; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; p, phosphorylated; THS, trauma-hemorrhagic shock.