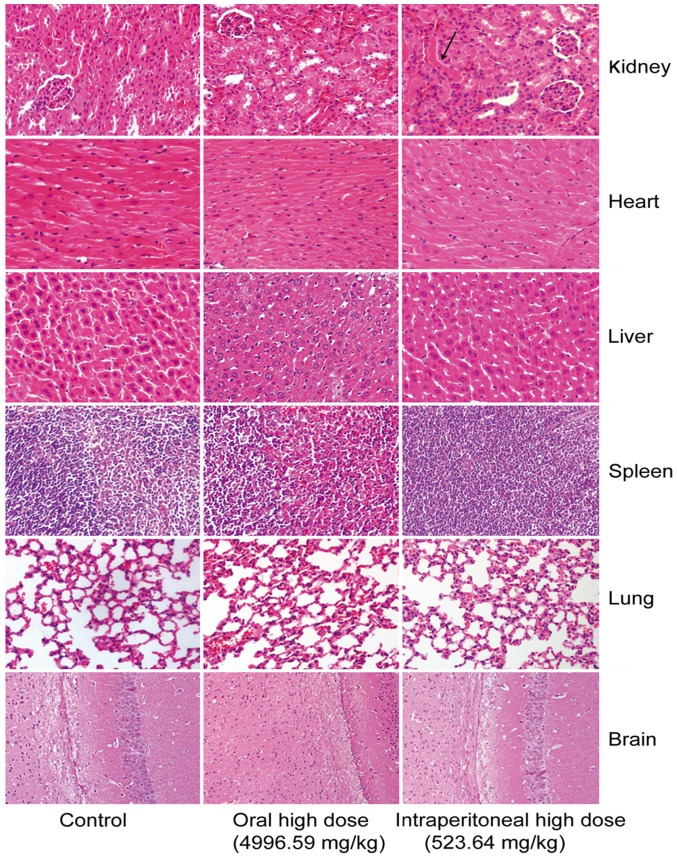
Figure 1.
Histological analysis of the digestive tract in mice. Oral medication and intraperitoneal injection groups exhibited marked mucous layer, epithelial cell and interstitial damage. Mice primarily suffered from mucosal necrosis, epithelial cell necrosis or erosion, interstitial hyperemia or bleeding, mucosal congestion and villous edema in the intestine. However, the groups exhibited different extents of gastrointestinal damage.