Figure 2.
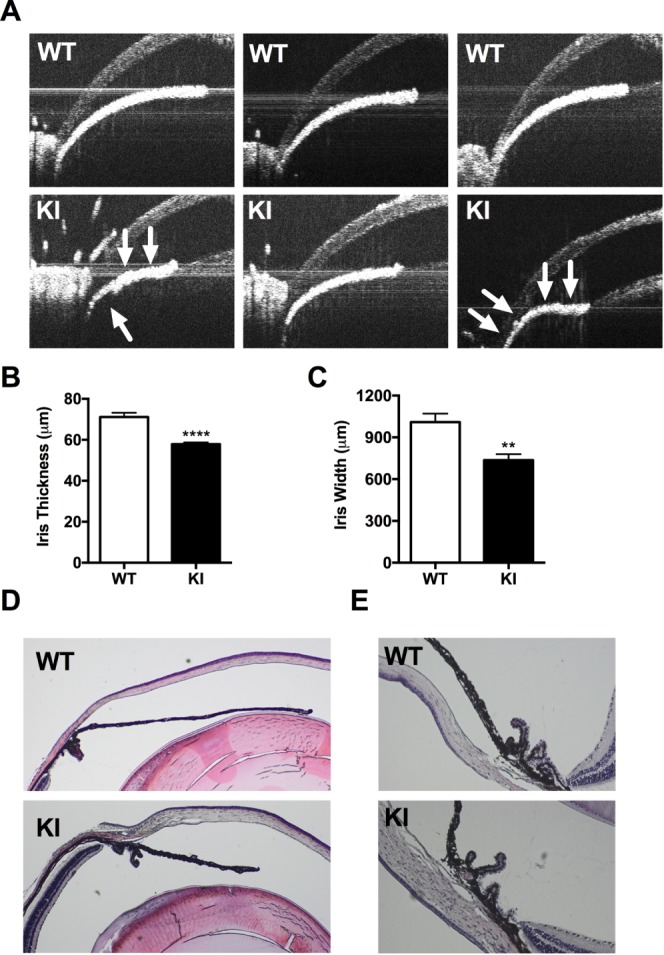
An Arg649Trp PIK3R1 mutation in mice replicates human iris morphology seen in affected individuals with SHORT syndrome. (A) A panel of OCT images showing the irides of WT control mice (top) and PIK3R1 knock-in mice (bottom). Note the thinner and shorter irides in the knock-in animals. Iris plateau formation and narrow chamber angle is marked with arrows. (B) Iris thickness and (C) iris width were quantified from the OCT images using the average of six independent measurements. (D) Hematoxylin- and eosin-stained sections of anterior eye in WT control mice (top) and mutant mice (bottom). (E) Close-up of iridocorneal angle shows similar morphology between the two groups. Results for width and thickness are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 7–13). **P < 0.01; ****P < 0.0005, unpaired Student's t-test.
