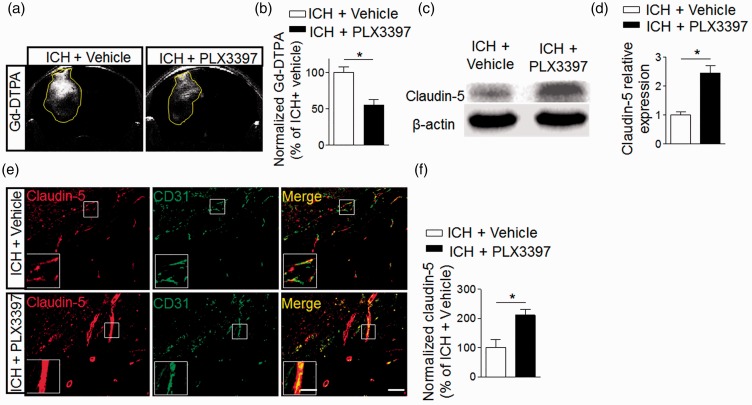
Figure 7.
CSF1R inhibition preserves the integrity of blood–brain barrier after ICH. ICH was induced by injecting 0.0375U collagenase. (a) MRI was performed to determine the permeability of the blood–brain barrier in ICH mice treated with PLX3397 or vehicle. Images were scanned under T1 sequence before and after injection of Gd-TDPA at day 3 after ICH. Gd-enhancement was calculated as follows: rT1% = (mean signal intensity of a region of the ipsilateral − mean signal intensity of the contralateral homologous normal brain area)/mean signal intensity of the contralateral homologous normal brain area. (b) Bar graph shows PLX3397 reduced Gd-enhancement at day 3 after ICH. Mean ± s.e.m. n = 3 mice per group from two independent experiments, *p < 0.05. (c) Western blot was performed to assess the expression of claudin-5 in the ipsilateral hemisphere of ICH mice treated with PLX3397 versus vehicle controls. (d) Bar graph shows higher expression level of claudin-5 in the ipsilateral hemisphere of ICH mice treated with PLX3397. n = 6 mice per group. (e) Brain sections from ICH mice treated with PLX3397 or vehicle were stained with CD31 (green) and claudin-5 (red) at day 3 after ICH. Scale bar: 50 µm; insert: 20 µm. (f) Summarized results show that ICH mice treated with PLX3397 had reduced claudin-5 loss in immunofluorescence intensity within the lesion area. Mean ± s.e.m. n = 12 sections from three mice per group from three independent experiments, *p < 0.05.