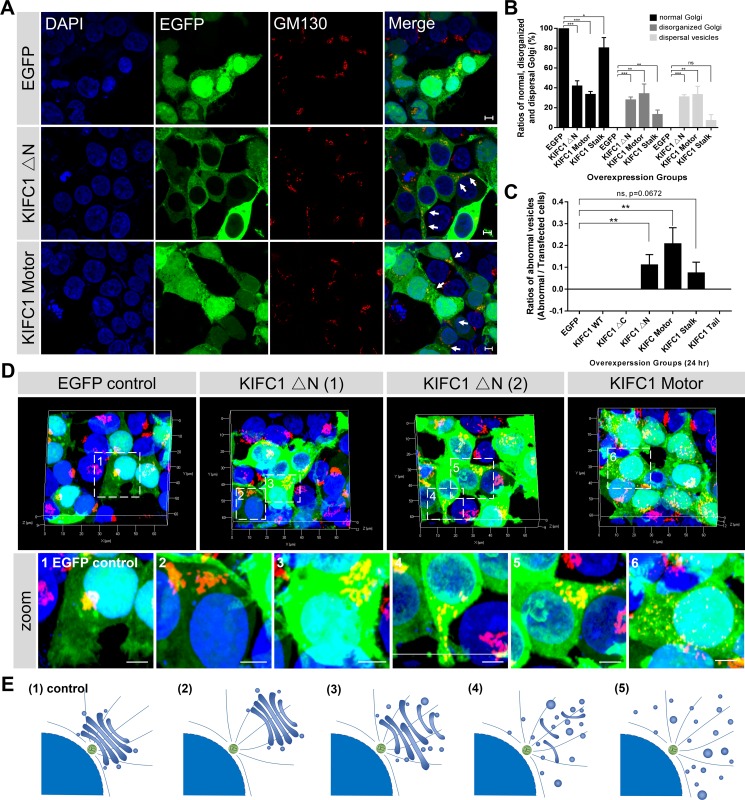
Figure 2. Dominant negative effects of KIFC1 ΔN and KIFC1 motor constructs on the Golgi apparatus.
See also Supplementary Figures 3, 4. (A) Representative confocal images shows the nucleus (DAPI), KIFC1 ΔN and KIFC1 motor EGFP fusion constructs (green) and the Golgi apparatus (GM130). Scale bars, 5 μm. (B) Quantification the normal Golgi, disorganized Golgi and scattered Golgi-associated vesicles in the transfected HEK293T cells after overexpression with EGFP control, KIFC1 ΔN, KIFC1 Motor and KIFC1 Stalk for 24 hr, respectively. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. (C) Quantification of the abnormal EGFP-accumulated vesicles in the transfected HEK293T cells after overexpression with each KIFC1 mutant construct, respectively, for 24 hr. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. (D) Three dimensional images of KIFC1 ΔN and KIFC1 motor constructs in HEK293T cells. DAPI (blue), EGFP fusion proteins (green), GM130 (red). The zoom indicates the magnified view of the outlined boxes. Scale bars, 5 μm. (E) (1) In the control, the Golgi apparatus is a single-copy ribbon-like organelle, which is closely associated with the centrosome near the nucleus. Overexpression of the KIFC1 ΔN and KIFC1 motor constructs results in several defects: (2) The Golgi apparatus seems normal, but located away from the nucleus; (3-4) The characteristic stacked Golgi morphology is aberrant and several Golgi cisterna are dispersed at the cytosol; (5) Many Golgi mini-stacks and cisternae are distributed throughout the cytoplasm.