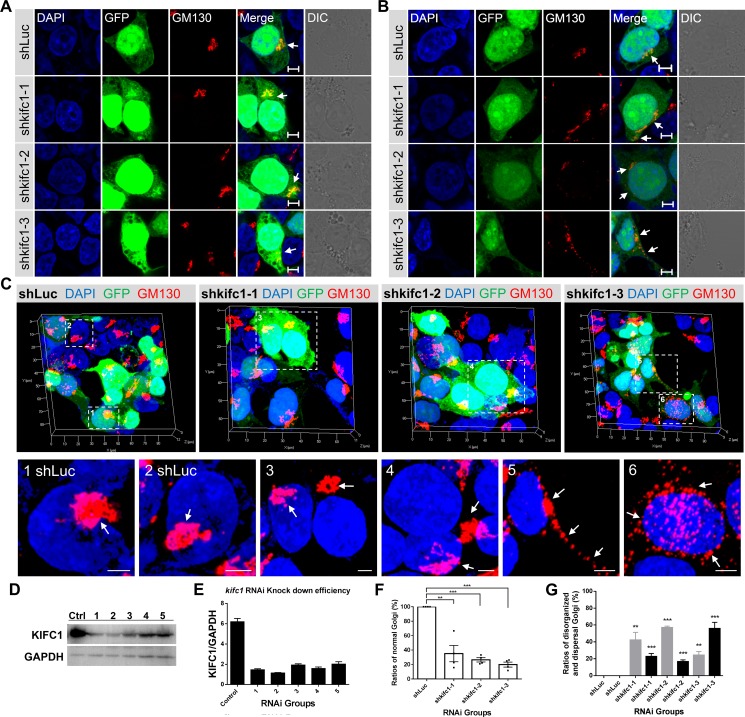
Figure 3. Depletion of KIFC1 led to the disorganization and dispersal of the Golgi apparatus.
(A, B) HEK293T cells were transfected with the shLuc, shkifc1-1, shkifc1-2, shkifc1-3 shRNA plasmids for 90 hr and analyzed by immunofluorescence assays, respectively. shLuciferase was used for the control group. DAPI (blue), GFP (green), GM130 (red), DIC (Differential Interference Contrast). Scale bars, 5 μm. (C) Representative three dimensional images of the Golgi apparatus (GM130, red) in the shRNA transfected HEK293T cells. The zoom is the magnified view of the indicated box. Scale bars, 5 μm. (D, E) Western Blot analysis of RNAi knockdown efficiency in HEK293T cells after 90 hr. Five different kifc1 targeting shRNA plasmids were used as candidates. The first, second and fourth plasmid (1, 2, 4 designated as shkifc1-1, shkifc1-2 and shkifc1-3, respectively) were selected for this study. GAPDH was used as the loading control. (F) Quantification the ratios of cells containing normal Golgi apparatus in the transfected HEK293T cells after kifc1 knockdown assay for 90 hr. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. ns, not significant; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 (Student's t-test). (G) Quantification of the ratios of disorganized Golgi apparatus (gray color) and the dispersed Golgi (black color) into vesicles after s after kifc1 knockdown assay for 90 hr. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. ns, not significant; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 (Student's t-test).