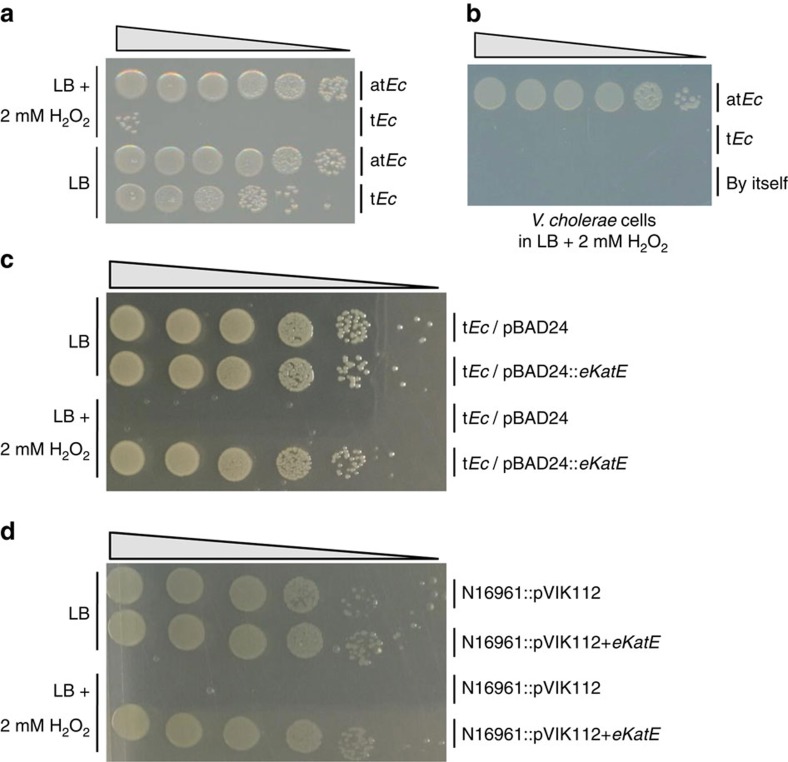
Figure 3. The atEc strain is resistant to H2O2.
(a) Viable cell numbers of atEc and tEc strains after growth in LB for 3 h in the presence (top two rows) or absence (bottom two rows) of 2 mM H2O2. Serial dilutions of bacterial cultures were spot-inoculated onto LB plates. (b) Viable cell numbers of Vc N16961. Overnight cultures of N16961 cells were diluted 100-fold in LB+2 mM H2O2 that had been precultured for 2 h with atEc or tEc. N16961 was grown for a further 4 h. The Vc CFUs in each culture were determined by growing serial dilutions on LB+200 μg ml−1 SM plates. (c) Viable cell numbers of tEc strains harbouring pBAD24 or pBAD24::eKatE after growth in LB for 3 h in the absence (top two rows) or presence (bottom two rows) of 2 mM H2O2. Serial dilutions of bacterial cultures were spot-inoculated onto LB plates. (d) Viable cell numbers of Vc N16961 strains with chromosomally integrated pVIK112 or pVIK112+eKatE plasmid after growth in LB for 3 hrs in the absence (top two rows) or presence (bottom two rows) of 2 mM H2O2. Serial dilutions of bacterial cultures were spot-inoculated onto LB+200 μg ml−1 SM plates.