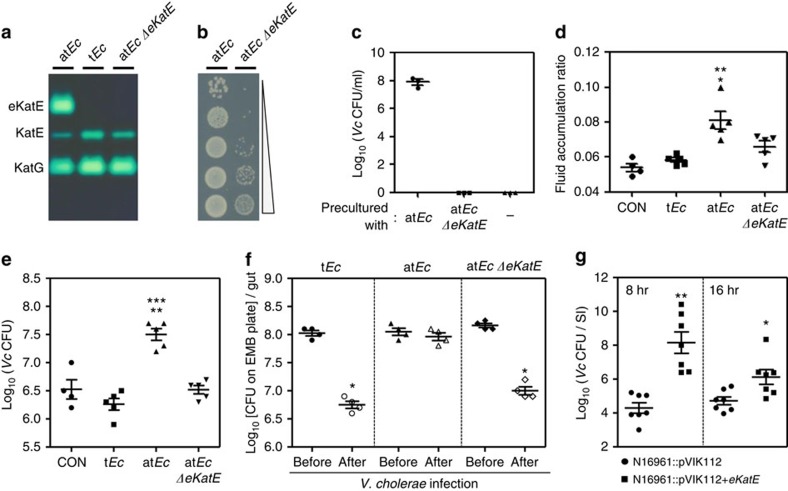
Figure 5. The eKatE-encoded catalase plays a critical role in atEc-mediated enhancement of Vc infectivity.
(a) Construction of an atEc eKatE deletion mutant. Bacterial extracts were loaded on a 7.5% nondenaturing polyacrylamide gel, electrophoresed to allow protein separation and then stained for catalase activity. (b) Serial dilutions of bacterial cultures (atEc strain and its ΔeKatE mutant) were inoculated onto LB plates after growth in LB+2 mM H2O2 for 3 h. (c) An overnight culture of N16961 was diluted 100-fold into LB+2 mM H2O2 that had been precultured for 2 h with atEc or its ΔeKatE counterpart. N16961 cells were grown for a further 4 h. Vc viability was determined by CFU counting. (d) Vc-induced FA ratios in groups of infant mice (n=5 per group) that had been transplanted with tEc, atEc or atEc ΔeKatE cells. Non-transplanted mice (n=4) were used for the control infection. **P<0.005 versus the FA ratio of the control or tEc-transplanted group. *P<0.05 versus the FA ratio of ΔeKatE-transplanted mice. (e) The numbers of Vc N16961 cells recovered from the intestines of each group are expressed as means±s.e.m. and are displayed on a log scale. **P<0.005 versus Vc CFUs from the control group. ***P<0.001 versus Vc CFUs from tEc-transplanted or ΔeKatE-transplanted mice. (f) The number of each E. coli strain recovered from infant mice (n=4 per group) before (solid) and after (open) Vc infection was determined; values are expressed as means±s.e.m. and are displayed on a log scale. *P<0.01 versus CFUs from the ‘before’ group. (g) Adult mice (n=14 per group) were infected with either Vc N16961::pVIK112 (circles) or N16961::pVIK112+eKatE (squares) by oral gavage. At 8 and 16 h post-infection, seven mice in each infection group were killed and bacterial numbers present in small intestine were determined. Values are expressed as means±s.e.m. **P<0.001, *P<0.05 versus control infection. Bacterial suspensions were prepared from mid-log phase cultures at ∼1014 per ml and 200 μl of suspensions were used for oral gavage.