Figure 5.
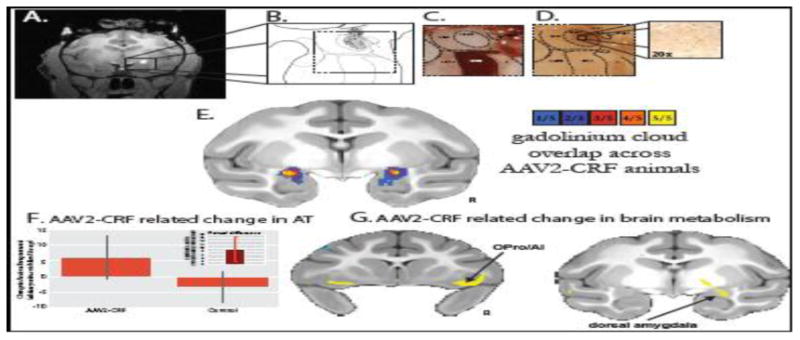
In vivo estimation and postmortem verification of dorsal amygdala corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) overexpression. (A) The gadolinium cloud in the dorsal amygdala, central nucleus (Ce) region, during and immediately following adeno-associated virus type 2 (AAV2)-CRF delivery provided an estimate of the location and extent of the infusions. (B) Camera lucida drawings of CRF expression from postmortem tissue reflected the extent of viral infusion as estimated from the intraoperative gadolinium signal. Gray regions represent neuropil staining and the black dots represent CRF overexpressing cells. (C) Acetylcholinesterase staining defined the boundaries of the amygdalar nuclei. (D) Adjacent sections were used for CRF immunohistochemistry demonstrating marked overexpression in the dorsal amygdala, Ce region. (E) Based on the intraoperative gadolinium images, we estimated the infusion extent in standard space to examine the overlap of the gadolinium injection clouds across the five experimental animals. The colors represent the number of animals with gadolinium signal at each voxel. Note the bilateral overlap across all experimental animals within the Ce region (yellow). (F) Compared with their matched control animals, the CRF overexpressing animals demonstrated increased postsurgical levels of AT (mean +/- SEM). Significance was determined using a paired-samples t-test comparing dorsal amygdala CRF animals and their cagemate control animals (CRF group [post-pre] – control group [post-pre]) (p<, .05, one-tailed; see inset and Kalin et al., (2016) for details). (G) Compared with their matched control animals, the CRF overexpressing animals demonstrated increased [post-pre] change in metabolism within the dorsal amygdala, OPro/AI, and hippocampus (yellow, p <, .01, two-tailed, uncorrected). ABmc, accessory basal nucleus, magnocellular subdivision; Astr, amygdalostriatal transition zone; Bmc, basal nucleus, magnocellular subdivision; CeLpc, central nucleus, lateral central subdivision; CeM, central nucleus, medial subdivision; L, lateral nucleus; R, right.
