Figure 1.
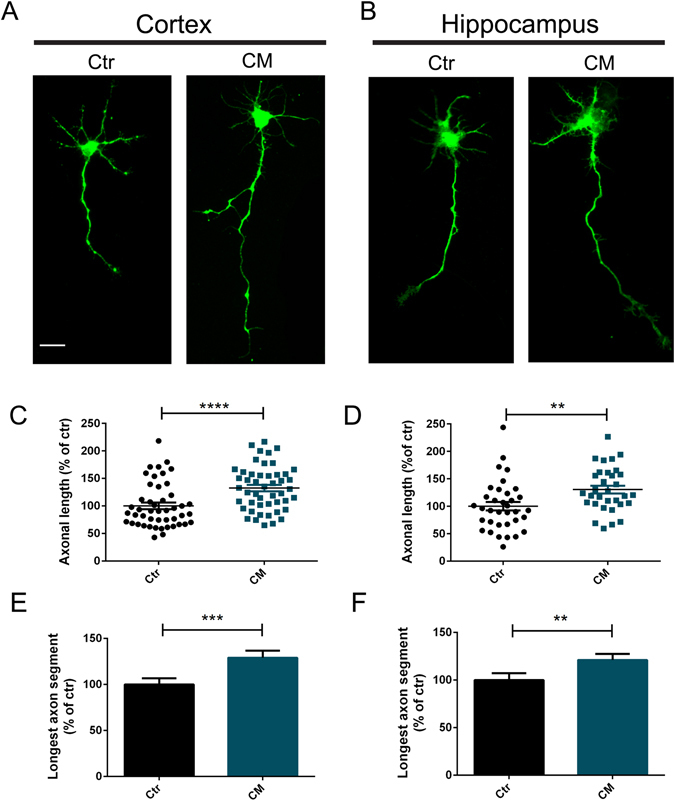
HUCPVC Conditioned Media (CM) induces axonal growth in CNS neurons. (A,B) Effect of CM in axonal outgrowth on cortical and hippocampal neurons. At DIV3 neurons were stimulated for 14 hours with CM. Axonal outgrowth was assessed by immunocytochemistry using an antibody against Tau, an axonal specific marker. Images were taken from random neurons using an AxioObserver Z1 fluorescent microscope with a PlanApochromat 20× objective. (C–F) Quantification of axonal length and axonal longest segment. Results show that axonal network increase after 14 h of CM stimulation (C,D), and in addition neurons stimulated with CM have the longest axonal segments (E,F), demonstrating that global application of CM to both hippocampal and cortical neurons induce an increase in axonal outgrowth. Axonal length and longest axonal segments analysis was performed with Image J 1.45e software. Bars and plots represent the mean ± SEM of approximately 45 neurons randomly selected of 3 independent experiments. (C) ****Represents p < 0.0001; (D) *Represents p = 0.0025; (E) ***Represents p = 0.0010; (F) *Represents p = 0.0083 by Mann Whitney unpaired t-test when compared to Ctr. The scale bar is 25 µm.
