Figure 8.
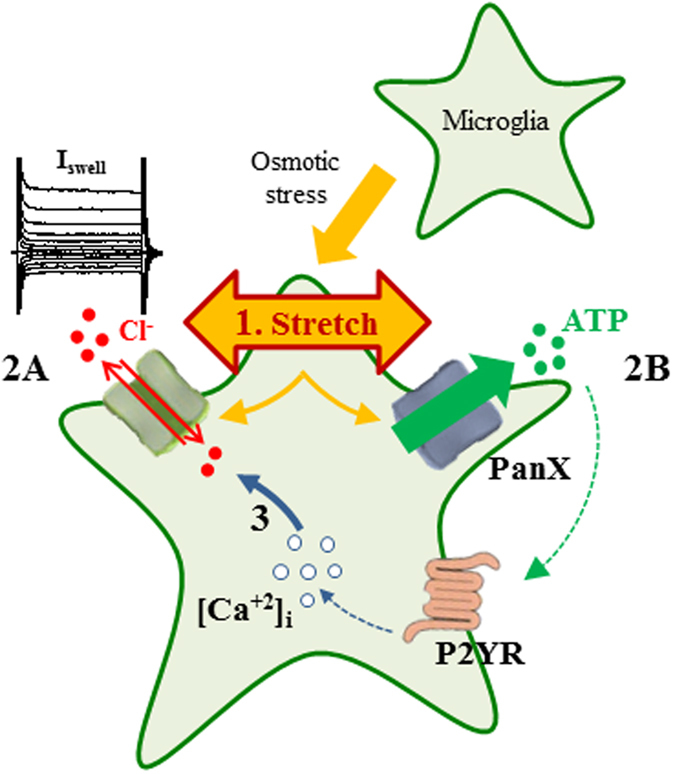
Model of the Ca2+ and ATP-dependent activation loop for hypotonic-induced currents in microglial cells. Osmotic stress causes cell swelling and a consequent membrane stretch (1), inducing a swell-dependent chloride current (2A) and ATP release through pannexin hemichannels (2B). ATP amplifies the current activation by binding to P2Y purinergic receptors (P2YR), possibly through Ca2+-dependent mechanisms. I Swell: swell-activated anionic channels; PanX pannexin1 hemichannels.
