Figure 1.
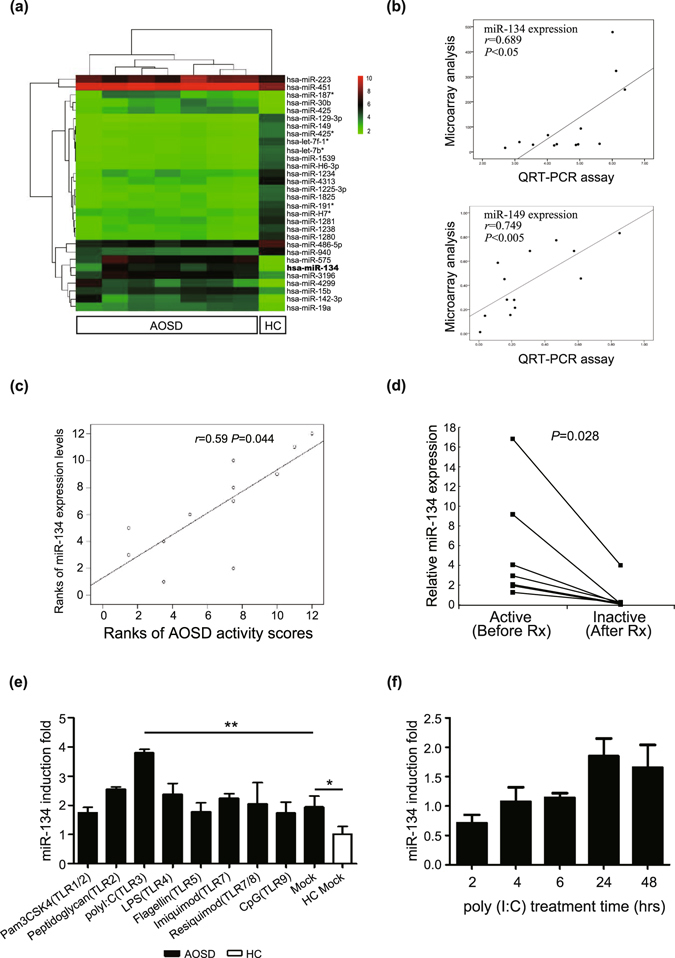
Increased microRNA-134 (miR-134) levels in patients with active adult-onset Still’s disease (AOSD) is associated with disease activity and induced by Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) ligand stimulation. (a) The differentially expressed microRNAs (miRNAs) in plasma from patients with AOSD and healthy controls (HC) identified using microarray analysis. Hierarchical clustering of miRNA profiles in AOSD patients group and HC group. Relative expression levels of miRNAs are depicted according to a color scale (red represents relative expression greater than the median expression level across all samples and green represents an expression level lower than the median). (b) Validation of miRNA microarray with quantitative reverse transcription PCR (QRT-PCR) for the two randomly selected differentially expressed miRNAs in AOSD patients. (c) A significant correlation between disease activity and miR-134 expression determined by QRT-PCR assay in AOSD patients. (d) Significant decreases in miR-134 expression levels paralleled the clinical remission in AOSD patients after 6 months of therapy. (e) Analysis of miR-134 expression in response to a panel of innate immunity Toll-like receptors (TLRs) ligands stimulation. The peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from patients with AOSD were treated with the indicated stimuli for 24 h. MiR-134 expression was analyzed by QRT-PCR and normalized using Rnu6 levels. (f) Kinetics of TLR3 ligand induction of miR-134.
