Figure 1.
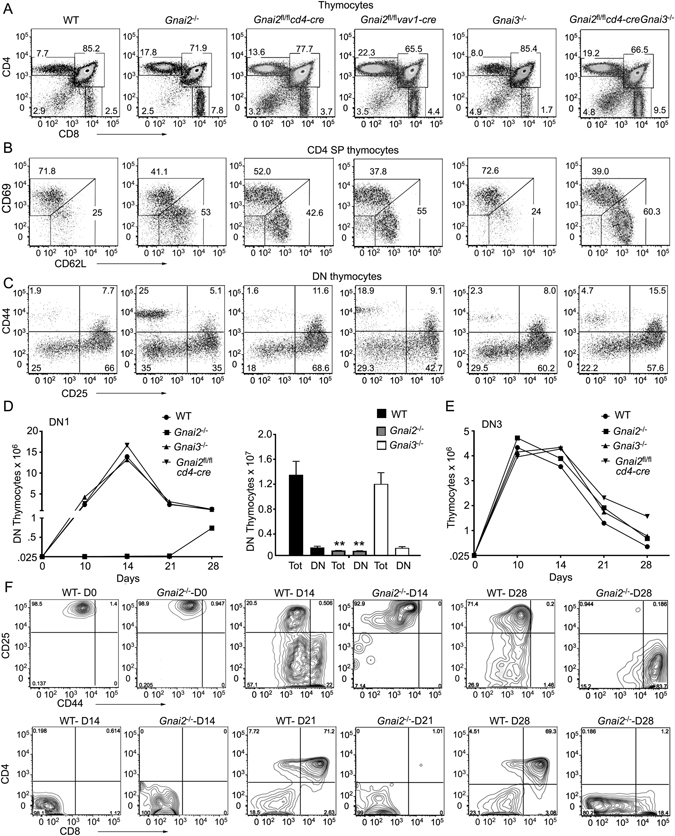
Loss of Gnai2 inhibits early thymocyte development and causes SP mature thymocytes to accumulate. (A) Representative flow cytometry of thymocytes from indicated mice examining CD4 versus CD8 expression. (B) Representative flow cytometry of thymocytes from indicated mice gated on CD4 SP thymocytes for their expression of CD62L and CD69. (C) Representative flow cytometry of thymocytes from indicated mice gated on DN thymocytes for their expression of CD44 and CD25. (D) Growth and differentiation of FACS sorted DN1(Lin−CD25− CD44+CD117+) thymocytes purified from the indicated mice and cultured on OP9-DL1 cells in the presence of IL-7 (1 ng/ml) for 28 days. The numbers of total and DN thymocytes recovered at Day 28 from each of the genotypes is shown to the right. (E) Growth of FACS sorted DN3 thymocytes from the indicated mice cultured on OP9-DL1 cells in the presence of IL-7 (1 ng/ml) for 7 days. Experiments were performed a minimum of 3 times. **p < 0.005 (Student’s t-test). (F) Representative flow cytometry plots from part D comparing WT and Gnai2 −/− DN1 thymocytes cultured for various durations on OP9-DL1 cells.
