Fig. 1.
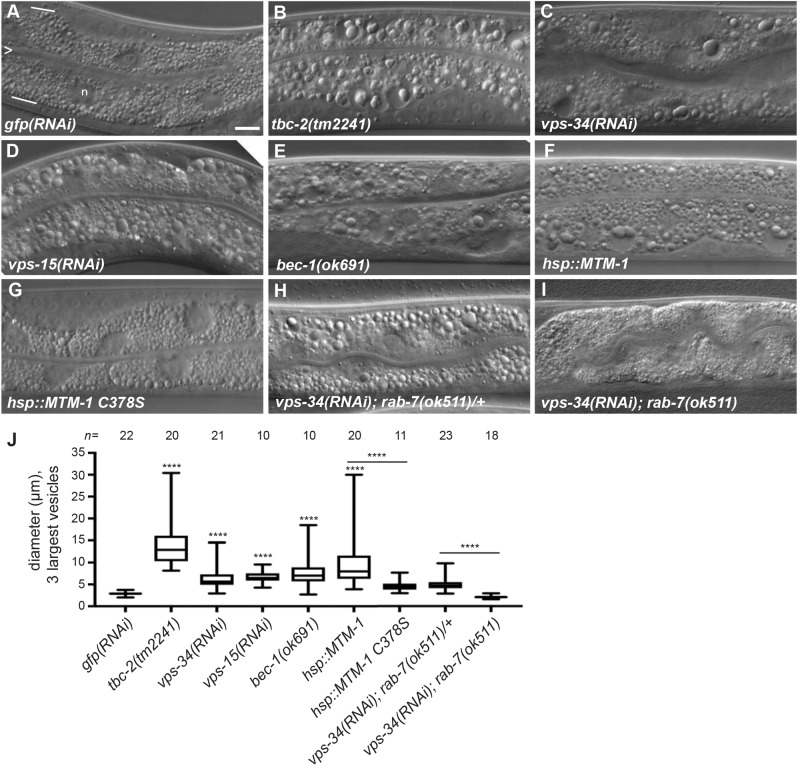
Loss of the VPS-34 PI3K complex or overexpression of the MTM-1 PI3 phosphatase causes a RAB-7-dependent large vesicle phenotype in the intestine. (A–I) Representative Nomarski differential interference contrast (DIC) images of the intestine of L4 stage larvae with genotype or RNAi expression: gfp(RNAi) (A), tbc-2(tm2241) (B), vps-34(RNAi) (C), vps-15(RNAi) (D), bec-1(ok691) (E), qxIs156[Phsp::mtm-1] (F), qxIs210[Phsp::mtm-1 C378S] (G), vps-34(RNAi); rab-7(ok511)/mIn1 (H), and vps-34(RNAi); rab-7(ok511) (I). For reference, the intestine is composed primarily of binucleate cells and is one cell in thickness. In A, the intestinal lumen is marked with an ‘>’ and represents the apical membrane, and white lines mark the basal membrane. Although not discernible, approximately four cells are present in each image. ‘n’ denotes a nucleus and is not to be confused with large vesicles. (J) Box-and-whisker plot of the diameters (µm) of the three largest vesicles in the intestines of the indicted genotypes and RNAi conditions. The box represents the 25–75th percentiles, and the median is indicated. The whiskers show the minimum to maximum of all data. ****P<0.0001 (unpaired t-test); all conditions were compared to control gfp(RNAi) unless indicated by a bar. n, number of animals scored. Scale bar: 10 µm.