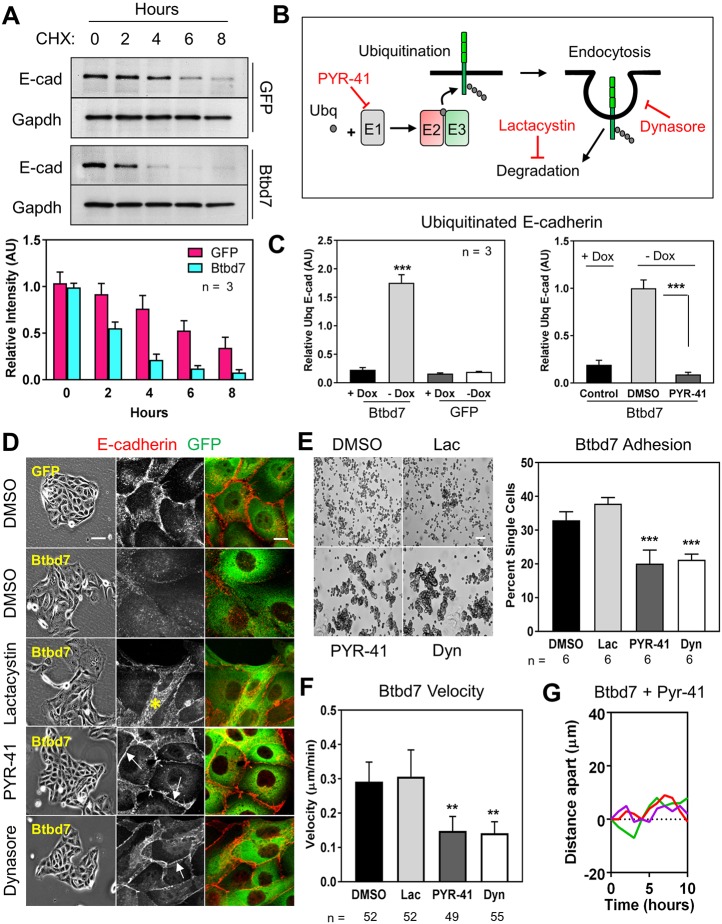
Fig. 6.
Btbd7 overexpression triggers increased E-cadherin internalization and degradation in MDCK cells. (A) E-cadherin turnover in the presence of cycloheximide is enhanced when Btbd7 is overexpressed. (B) Schematic of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway and pharmacological inhibitors used. (C) E-cadherin was immunoprecipitated from GFP and GFP-Btbd7-overexpressing MDCK cells, and western blots were probed for ubiquitin. Btbd7 overexpression resulted in increased ubiquitin levels on immunoprecipitated E-cadherin (Btbd7-Dox), which could be blocked by treatment with the ubiquitylation inhibitor PYR-41 (right panel). (D) Inhibition of ubiquitylation with PYR-41, endocytosis with dynasore, but not proteasomal degradation with lactacystin, partially rescue E-cadherin localization (gray) at cell-cell junctions (white arrows) in Btbd7-overexpressing MDCK cells. Instead, treatment with lactacystin only increased intracellular E-cadherin (yellow asterisk). (E,F) Treatment with these same inhibitors also partially rescues the cell-adhesion (E) and migration (F) phenotypes of Btbd7-overexpressing cells. (G) Inhibition of ubiquitylation with PYR-41 also decreased the enhanced dynamics of adjacent cells within an island (compare with Fig. 5E). Scale bars: 50 µm in E; 10 µm in D. Data are mean±s.d. with n indicated below the x-axis. One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test; **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.