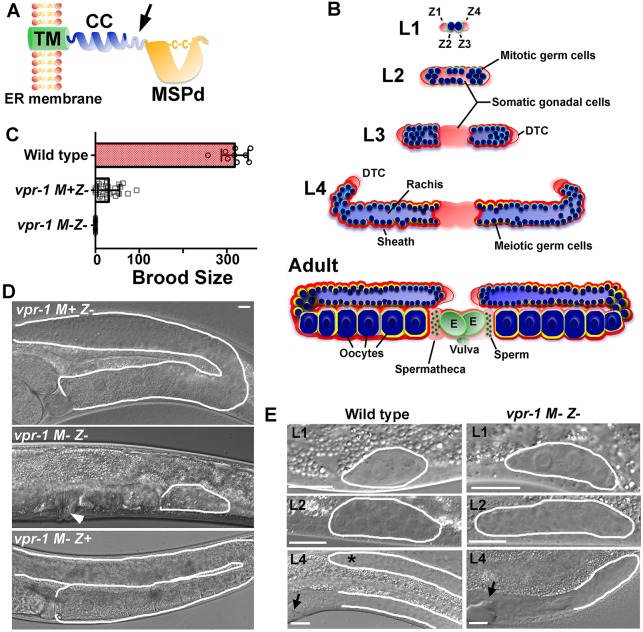
Fig. 1.
C. elegans vpr-1 null mutants are maternal effect sterile. (A) VAP structure showing major sperm protein domain (MSPd), coiled-coil motif (CC) and transmembrane domain (TM). VAPs are type II membrane proteins with the TM spanning the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and MSPd in the cytosol. Arrow indicates approximate (unknown) site of proteolytic processing, which liberates the MSPd for secretion. (B) Postembryonic gonad development showing larval stages (L1-L4) and adult structure. The gonad primordium in freshly hatched embryos consists of the germline precursors Z2 and Z3 (dark blue) and the somatic gonad precursors Z1 and Z4 (pale red). The distal tip cell (DTC) migrates during larval development to form the U-shaped gonad arms. The DTC also expresses the Notch ligand LAG-2, which acts through the GLP-1 receptor to control germ cell proliferation and meiotic entry (Hansen and Schedl, 2013). Germ cells enter meiosis (blue circles with yellow outline) during the L4 stage, forming sperm first and then oocytes in adulthood. Sperm are stored in the spermatheca and embryos (green, E) in the uterus. (C) Average brood sizes of wild-type and vpr-1 mutant hermaphrodites lacking zygotic (Z−) or maternal and zygotic (M− Z−) expression. Error bars are s.d. N=9 for wild type, N=26 for vpr-1 M+ Z− and N=50 for vpr-1 M− Z−. (D) DIC images of vpr-1 mutant adult hermaphrodite gonads. Arrowhead points to the vulva, which is induced by the anchor cell. (E) DIC micrographs of wild-type and vpr-1 mutant gonads during larval stages. Asterisk indicates the elongating distal gonad arm. Arrows point to developing vulva (left). Gonads are outlined in white. Scale bars: 10 µm.