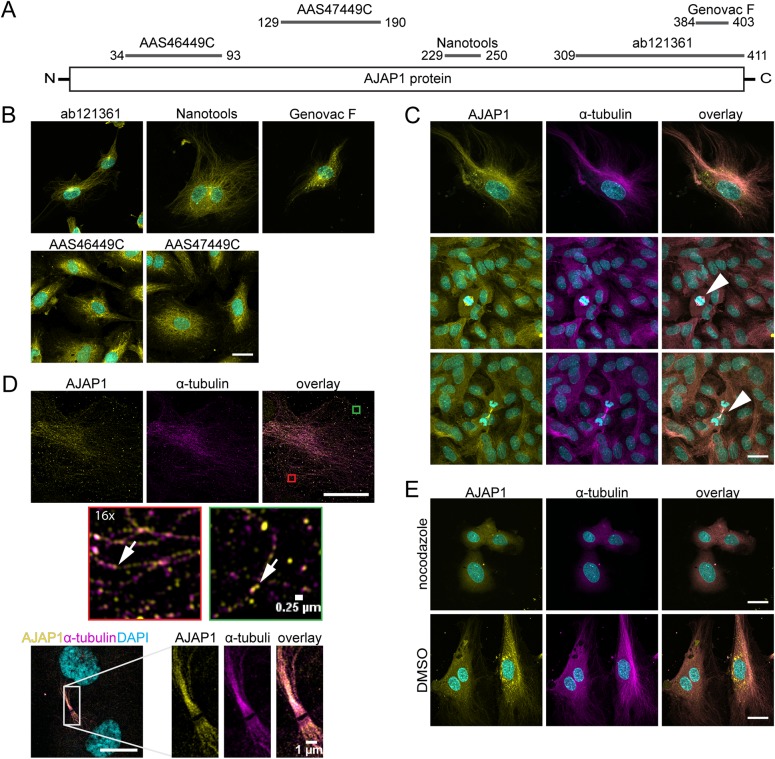
Fig. 3.
AJAP1 co-localizes with microtubules in HUVECs. (A) Schematic overview of the epitope binding sites for antibodies used to detect AJAP1 in HUVECs. The antibody recognition sites are mapped to the polypeptide chain. The numbers indicate the amino acid positions on the AJAP1 polypeptide chain. (B) Detection of AJAP1 (yellow) using antibodies with different epitope recognition sites shows fibrillar structures in HUVECs. Cell nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (cyan). Scale bar: 25 µm. (C) Immunostaining of AJAP1 (Genovac antibody, yellow) and α-tubulin (magenta) shows AJAP1's association with microtubules in HUVECs. The microtubule association is independent from the confluence of the culture. HUVECs were grown until confluence and fixed after seven days. AJAP1 is additionally localized to microtubules contributing to the spindle apparatus during cell division (arrowhead). Further, numerous AJAP1-positive puncta are localized in the perinuclear region. Cell nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (cyan). Microscope: Zeiss LSM 780; objective lens: Plan-Apochromat 63×/1.40 Oil DIC M27; scale bar: 25 µm. (D) Structured illumination microscopy (SIM) gives a detailed view of the co-localization of AJAP1 and microtubules in HUVECs. AJAP1 localizes in close proximity to the tubular network lining the fibers (arrows). During mitosis and cell division, AJAP1 co-localizes with the spindle apparatus. Microscope: Zeiss Elyra; objective lens: Plan-Apochromat 63×/1.4 Oil DIC M27; scale bar: 25 µm (upper panel) and 10 µm (lower panel). (E) The association of AJAP1 with microtubules in HUVECs is lost upon microtubule destruction. Treatment with 12.5 µM nocodazole for 24 h shows destruction of the microtubule network and loss of AJAP1 tubular localization. For a negative control, HUVECs are treated with DMSO for 24 h. Cell nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (cyan). Microscope: Zeiss LSM 780; objective lens: 63×/1.40 oil; scale bar: 25 µm.