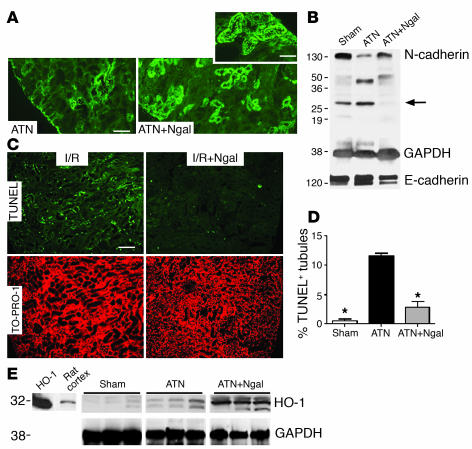
Figure 4.
Correlates of ATN. Kidneys were harvested 24 hours after reperfusion. (A) N-cadherin staining was nearly abolished by ischemia-reperfusion (ATN), but it predominated apical cell-cell junctions after treatment (100 μg holo-Ngal; ATN+Ngal). (B) Full-length N-cadherin (130 kDa) was rescued by Ngal. Note the presence of N-cadherin fragments (28 kDa) in ischemia-reperfusion and sham-treated animals, but their suppression in Ngal-treated animals (arrow). In contrast, there was little change in the level of E-cadherin protein. GAPDH (38 kDa) was the loading control. (C) Tubules with TUNEL+ apoptotic cells (green fluorescence in ischemia-reperfusion injury; I/R) were reduced by pretreatment with Ngal (I/R+Ngal). TO-PRO-l was the nuclear counterstain (red) for the same field. (D) Percentage of tubules containing at least 1 apoptotic nucleus. Ischemia-reperfusion injury increased the number of positive tubules 22-fold, and Ngal reduced the activity fourfold. *P < 0.001 vs. I/R. (E) Ngal upregulated HO-1 (32 kDa) expression in ischemic kidneys. Kidneys harvested 24 hours after ischemia-reperfusion (ATN) expressed HO-1, but when animals were treated with Ngal, HO-1 expression was enhanced (ATN+Ngal). Purified HO-1 (HO-1) and rat cortex are included for comparison. GAPDH was the loading control. Scale bars: A and C, 9 μm; A, inset, 4.6 μm.