Figure 1.
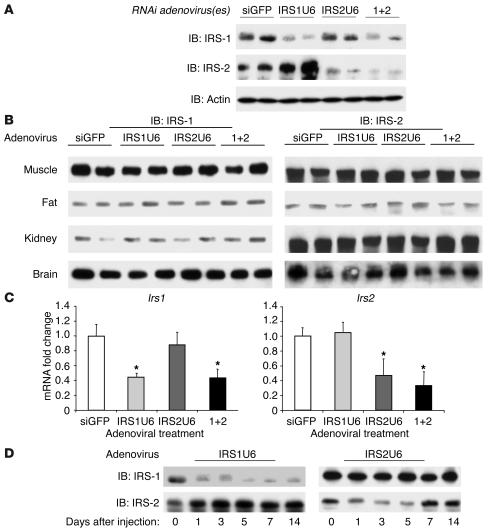
RNAi adenoviruses cause substantial and specific knockdown of IRS-1 and IRS-2 in liver. (A) Western blots for IRS-1, IRS-2, and actin in liver lysates from mice treated with siGFP, IRS1U6, IRS2U6, or both IRS1U6 and IRS2U6 (1+2). Livers were collected from mice after an overnight fast, and proteins were extracted and processed as described in Methods. Each lane represents liver lysates from a different mouse. (B) Muscle, fat, kidney, and brain lysates of the mice represented in A were subjected to immunoblots for IRS-1 and IRS-2. (C) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of IRS-1 and IRS-2 mRNA levels in livers 5 days after treatment with siGFP, IRS1U6, IRS2U6, or both viruses simultaneously (n = 6). Total RNA was extracted from livers and made into cDNA, and primers specific to IRS-1 and IRS-2 were used to determine levels of expression, as described previously (58). (D) Time course of effect of RNAi adenovirus. Liver lysates were made from mice 1, 3, 5, 7, or 14 days after viral injection and blotted for IRS-1 and IRS-2 proteins levels. Day 0 liver lysates were obtained from age-matched mice injected with saline. These results are representative of 3 independent experiments.