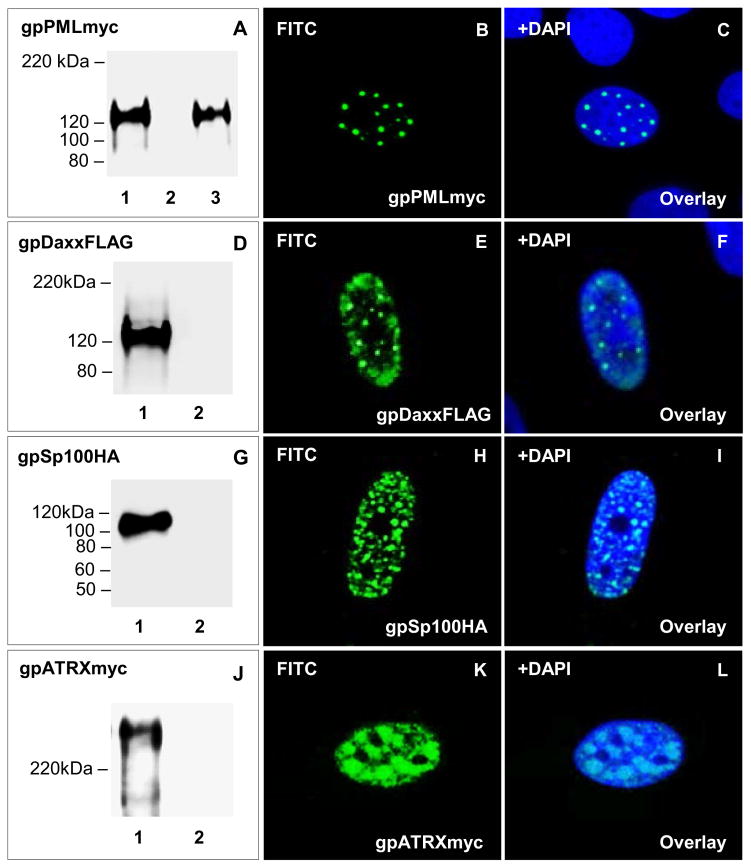
Figure 4. Transient expression and nuclear localization of guinea pig ND10 components.
Transient expression of ND10 fusion proteins in GPL cells confirmed by western blot analysis and immunofluorescence. Lane 1, individually transfected plasmids. Lane 2, mock transfected GPL cells. Lane 3, GPCMV infected cells plus gpPML. A–C, transient expression and localization of gpPMLmyc. A shows levels of gpPMLmyc in transiently transfected GPLs in the absence or presence of GPCMV. Mock infected cells or cells infected with GPCMV (1.5 MOI) were transiently transfected with gpPMLmyc expression plasmid. B shows expression for gpPMLmyc, with C being the overlay of B with DAPI. D–F, transient expression and localization of gpDaxxFLAG. D shows levels of gpDaxxFLAG in transiently transfected GPLs. E shows localization of gpDaxxFLAG, with F being the overlay of E with DAPI. G–I, transient expression and localization of gpSp100HA. G shows levels of gpSp100HA in transiently transfected GPLs. H shows localization of gpSp100HA, with I being the overlay of H with DAPI. J–L, transient expression and localization of gpATRXmyc. J shows levels of gpATRXmyc in transiently transfected GPLs. K shows localization of gpATRXmyc, with L being the overlay of K with DAPI. gpPMLmyc, gpDaxxFLAG, gpSp100HA, and gpATRXmyc detected by primary anti-epitope Ab and secondary anti-mouse or anti-rabbit IgG-HRP (western blot) and anti-mouse or anti-rabbit IgG FITC (immunofluorescence).