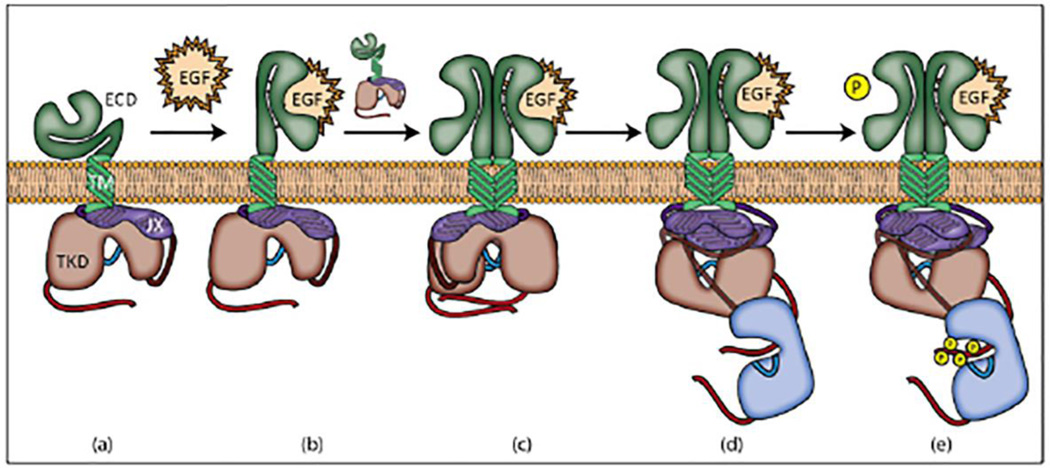
Figure 4.
Steps in EGFR activation. (a) Inactive EGFR. (b) EGFR is activated upon ligand binding. This induces a conformational change in extracellular domains I, II, and III. (c) The activated receptor dimerizes with another EGFR monomer driven by extracellular interactions. Domains I and II contribute to the binding site for EGF, and domain II contributes the dimerization interface; binding of a single EGF ligand to the activated dimer represents negative cooperativity when EGFR is in this state [2]. (d) Intracellular region then assumes the asymmetric kinase conformation. (e) The receiving receptor (blue) trans-phosphorylates tyrosine residues in the activating receptor’s (red) tail region.