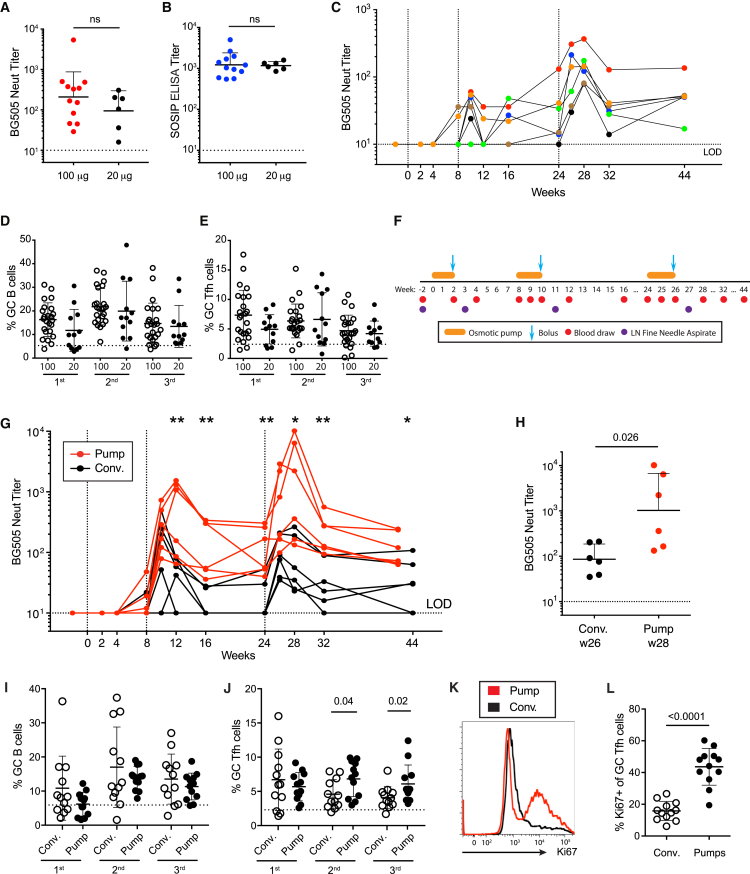
Figure 4.
Extended Immunogen Release Induces Higher nAb Titers Than Conventional Immunization
(A–E) Immunogen doses of 100 or 20 μg s.c. immunizations of BG505 SOSIP.664. (A) BG505 nAb titers at week 26 (n = 6 or 12). (B) BG505 SOSIP binding titers at week 26 (n = 6 or 12). (C) Kinetics of BG505 nAb titers. (D and E) GC B cell (D) and GC Tfh cell (E) frequencies after the first, second, and third immunizations.
(F–L) Bolus (conventional) versus continuous immunogen delivery of BG505 SOSIP.v5.2 immunogen. (F) Immunization schedule and sampling for continuous antigen delivery using osmotic pumps. (G) BG505 nAb titers in animals immunized by osmotic pump (red) or conventional bolus (Conv, black) (∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; n = 6). (H) Peak BG505 nAb titers after the third immunization (n = 6). (I and J) GC B cell (I) and GC Tfh cell (J) frequencies after the first, second, and third immunizations. (K) Proliferation of GC Tfh cells at week 11. Flow cytometry was gated on CXCR5hi PD-1hi GC Tfh cells. (L) Frequency of Ki67+ GC Tfh cells at week 11 (n = 12).
All nAb titer and ELISA binding Ab data represent geometric mean titers with geometric SD. All cell-frequency data represent the mean and SD. See also Figure S4.