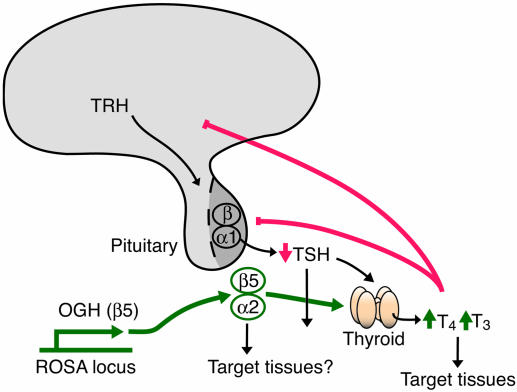
Fig. 4.
Pathways by which OGH may affect metabolism and weight loss. Stimulatory pathways from OGH-Tg are shown in green, feedback inhibition is shown in red, and normal physiological function is shown in black. Deletion of OGH does not modify thyroid function and hormone levels, but overexpression of OGH results in thyroid stimulation and increased T4/T3 levels. This increased thyroid tone may act on target tissues like muscle, liver, or adipose tissue to induce resistance to diet-induced obesity marked by increased basal metabolic rate, or OGH may act directly on target tissues.