Figure 3.
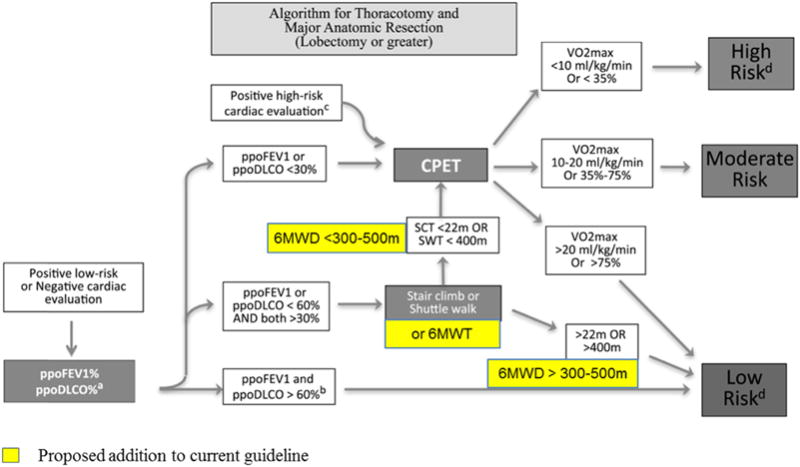
Proposed addition of the 6MWT to the physiologic evaluation of patients with lung cancer for further studies. 6MWD, 6-minute walk distance; 6MWT, 6-minute walk test; DLCO, diffusion capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide; FEV1, forced expiratory volume in 1 second; ppoDLCO predicted postoperative DLCO; ppoFEV1, predicted postoperative FEV1; SCT, stair-climbing test; SWT, shuttle walk test; , maximal oxygen consumption. (a) For pneumonectomy candidates, perfusion scan is suggested to calculate ppoFEV1 or ppoDLCO (ppo values = preoperative values ×(1 − fraction of total perfusion for resected lung). For lobectomy patients, segmental counting is indicated to calculate ppoFEV1 or ppoDLCO (ppo values = preoperative values ×(1 − y/z), where y is the number of functional or unobstructed lung segments to be removed and z is the total number of functional segments. (b) Cutoff chosen based on indirect evidence and expert consensus opinion. (c) For patients with a positive high-risk cardiac evaluation deemed to be safe to proceed to resection, both pulmonary function test and cardiopulmonary exercise test are suggested for a more precise definition of risk. (d) Definition of risk: Low risk: The expected risk of mortality is below 1%. Major anatomic resection can be safely performed in this group. Moderate risk: Morbidity and mortality rates may vary according to the values of split lung functions, exercise tolerance, and extent of resection. Risks and benefits of the resection should be thoroughly discussed with the patient. High risk: The risk of mortality after standard major anatomic resection may be higher than 10%. Considerable risk of severe cardiopulmonary morbidity and residual function loss is expected. Patients should be counseled about alternative surgical (minor resections or minimally invasive surgery) or nonsurgical options.32 Modified from Brunelli et al.32 with permission.
