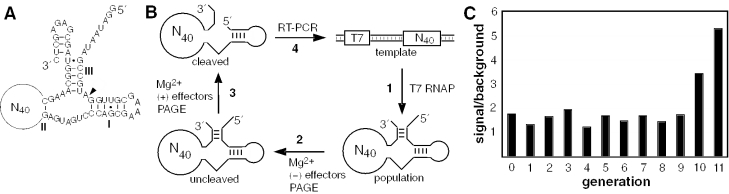
Figure 1.
Allosteric selection of allosteric hammerhead ribozymes that respond to cations. (A) RNA construct used for in vitro selection of allosteric ribozymes. The hammerhead ribozyme core is identical to that described previously (21). A 40 nt random-sequence domain (N40) replaces the majority of stem II of the hammerhead ribozyme core. The site of ribozyme cleavage is indicated by the arrowhead. (B) Scheme for the isolation of cation-dependent ribozymes by allosteric selection. Each population of ribozyme variants is prepared by transcription in vitro (1), subjected to negative (2) and positive (3) selections, and the cleaved RNAs that are enriched for allosteric function are amplified by RT–PCR (4). (C) Progress of the allosteric selection process. Values for signal and background reflect the fraction of RNA cleaved at step 3 in the presence or absence of the cation effector mixture, respectively. A ratio of 1 is expected if the addition of the cation mixture has no effect on ribozyme activity.