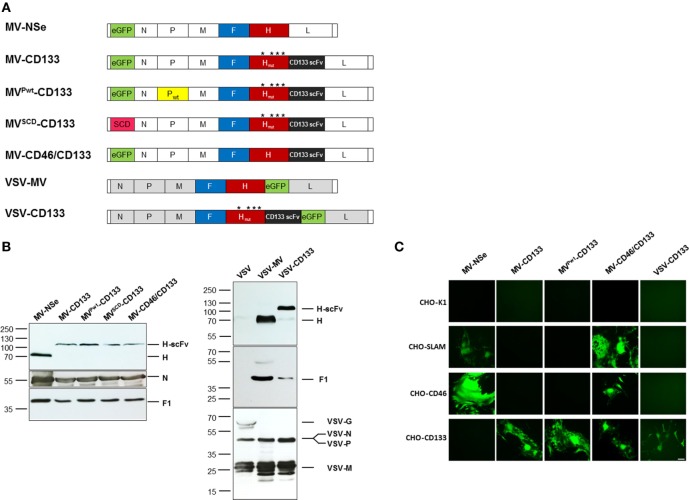
Figure 1.
Generation of CD133-targeted oncolytic viruses. (A) Schematic overview on the genomic organization of the OVs used in this study. Point mutations in H protein introduced to ablate natural receptor usage are indicated by asterisks. (B) Immunoblot showing the incorporation of measles virus glycoproteins into recombinant measles virus (MV) and vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) particles. Supernatants of Vero-αHis cells infected with the indicated viruses were denatured followed by fractionation by SDS-PAGE. Viral glycoproteins were detected with polyclonal antibodies directed against the indicated proteins. The parental MV-NSe, respectively, VSV and VSV-MV served as unmodified controls. N blots were used as loading control in both cases. (C) A panel of receptor-transgenic Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells (as indicated) was infected with MV-NSe, MV-CD133, MVPwt-CD133, MV-CD46/CD133, or VSV-CD133 at an MOI of 0.03. CHO-K1 served as receptor-negative cell line. GFP-fluorescent images were taken 72 h postinfection; Scale bar, 200 µm.