Figure 4.
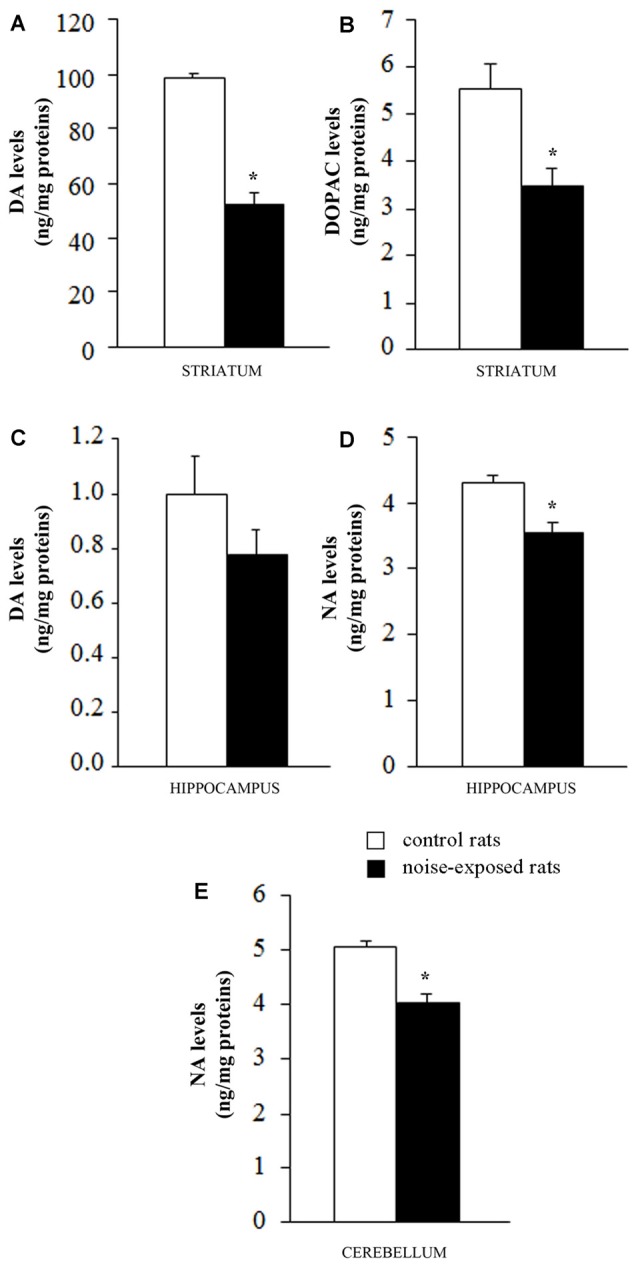
Loud noise exposure produces long-lasting (7 days), site-specific catecholamine loss. Graphs show catecholamine levels measured after noise exposure in specific brain areas: (A) dopamine (DA) and (B) 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC) levels in striatum; (C) DA levels in hippocampus; (D) noradrenaline (NA) levels in hippocampus and (E) cerebellum. White column = control rats; black column = 12 h noise-exposed rats sacrificed 7 days after exposure. *p ≤ 0.05 compared with controls.
