Figure 1.
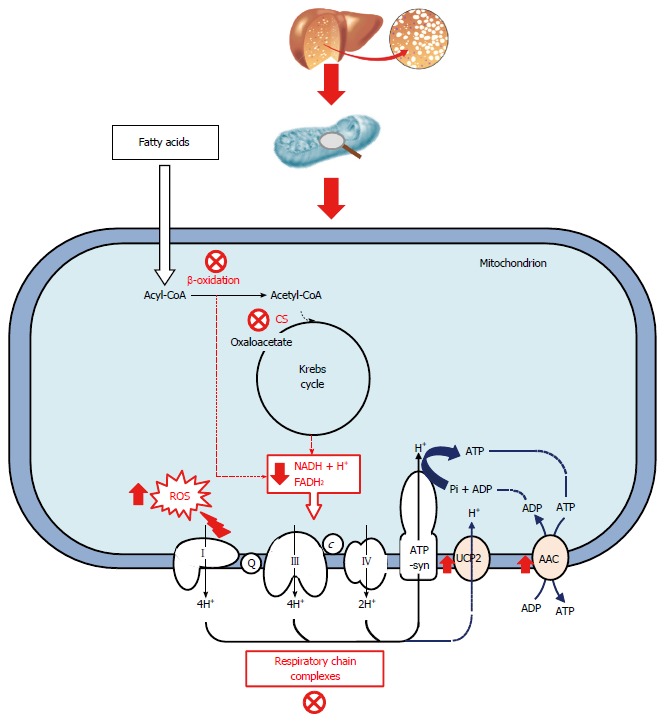
Dysfunctional mitochondrial bioenergetics in the fatty liver. In fatty liver, inhibition of β-oxidation and the reduction in citrate synthase (CS) activity implies a reduction in the flux of reducing equivalents to mitochondria. Mitochondrial respiration efficiency was decreased and this effect could be due to a possible uncoupling effect between ATP synthesis and transport through respiratory complexes. Alteration in mitochondrial function leads to increased ROS production. c: Cytochrome c; Q: Ubiquinone.
