Figure 10.
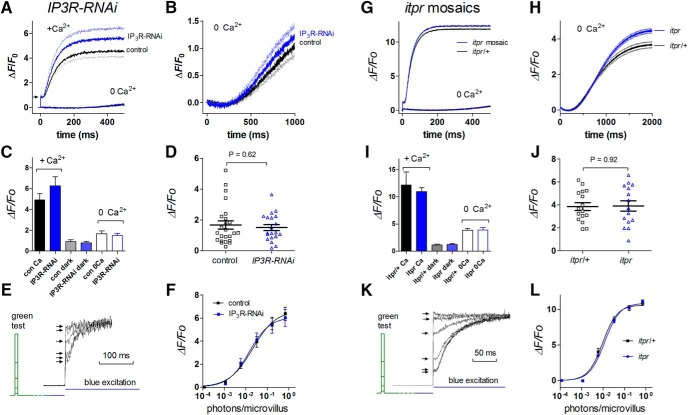
GCaMP6f signals are unaffected in IP3R-RNAi and itpr mutant flies. A, Average traces of GCaMP6f fluorescence in the presence (1.5 mm) and absence of Ca2+ (perfusion from puffer pipette with 0 Ca2+ 1 mm EGTA) from dissociated ommatidia from flies expressing GMRGal4;UAS-GCaMP6f and two copies of UAS-IP3R-RNAi (mean, n = 15) and control (GMRGal4;UAS-GCaMP6f alone; n = 9 ommatidia); pale traces indicate SEM. ΔF/F0 values for both +Ca2+ and 0 Ca2+ traces were based on F0 values in Ca2+-free solution. B, Ca2+-free responses on expanded scale. C, Summary of ΔF/F0 values measured 1 s after light onset, as well as the dark-adapted level in the presence of Ca2+ estimated from the “pedestal” (arrow in A). D, Ca2+-free ΔF/F0 values replotted, showing all data points: there was no significant difference (p = 0.62, two-tailed unpaired t test) between control and IP3R-RNAi flies. E, Two-pulse paradigm to determine intensity dependence of GCaMP6f signal in vivo from the deep pseudopupil (representative raw traces). Blue excitation was used to measure instantaneous GCaMP6f signal (arrows) in response to green (540 nm) test flashes (2 ms) of variable intensity delivered 300 ms earlier. F, Resulting intensity dependences of GCaMP6f signal in IP3R-RNAi (two copies) and control flies (GMR/+; UAS-GCaMP6f) were essentially identical (mean ± SEM, n = 8 flies). G–L, Similar data from itpr-null mosaics and sibling controls (itpr/+) expressing GCaMP6f under direct control of the Rh1 promoter (ninaE-GCaMP6f): n = 10–15 ommatidia/flies. No significant effects of the itpr–null mutation were detected.