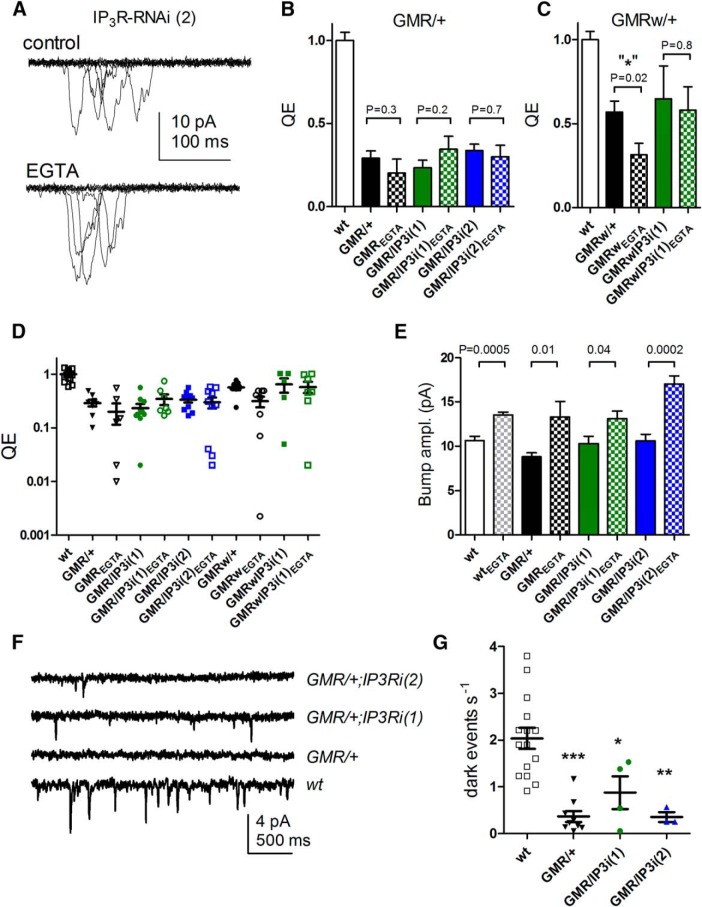
Figure 3.
GMRGal4 phenotypes in whole-cell recordings of light-induced currents. A, Quantum bumps (10 superimposed traces, including “failures”) in response to dim flashes containing on average ∼0.5 effective photons recorded from GMR/+;IP3R-RNAi (two copies) photoreceptors with control electrode solution and with 1 mm EGTA (below). Note larger amplitudes with EGTA electrode (see also E). B, C, QE determined from such recordings, normalized to wild-type (n = 20), in flies expressing one copy of GMRGal4 (GMR/+ or GMRw/+) with or without UAS-IP3R-RNAi (one or two copies) and with or without 1 mm EGTA in the electrode (mean ± SEM, n = 5–10 cells per condition; see D). All lines with one copy of GMRGal4 had reduced QE compared with wild-type (p < 0.001, one-way ANOVA, Dunnett’s multiple comparison), but inclusion of EGTA made little or no difference: one exception (in C) was in flies with one copy of GMRw but without IP3R-RNAi. This was marginally significant (p = 0.02) with a direct t test, but not with a one-way ANOVA including data with and without EGTA from GMRw/IP3R-RNAi flies as well. D, Same data showing QE in all cells on log10 plot: note variability in all GMRGal4/+ backgrounds (total n = 78 cells): whereas most cells had QE two- to fourfold lower than in wild type, 11 cells had ≥10-fold lower QE. E, Bump amplitudes were larger in recordings made with 1 mm EGTA in the electrode in all backgrounds (mean ± SEM of average bump amplitudes from n = 4–10 cells, each with 30–100 bumps). F, Dark noise recorded with standard electrode solution (no EGTA). In wild-type cells, spontaneous ∼2-pA events occur at rates of ∼2/s, but backgrounds with one copy of GMRGal4 (with or without IP3R-RNAi) showed far fewer events. G, Summary of data: all lines with one copy of GMRGal4 (GMR/+) had significantly fewer dark events than wild type (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001), but there was no significant effect of one or two copies of UAS-IP3R-RNAi (one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s posttest).