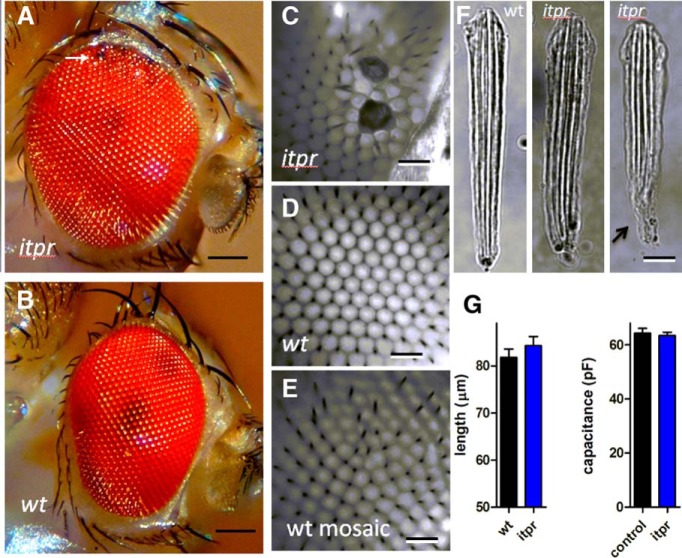
Figure 5.
Structural abnormalities in itpr mosaic eyes. A, itpr mosaic eyes were noticeably larger and rounder in appearance than wild type (B, D) and frequently had areas of irregular and/or blackened facets (detail in C, D). E, Wild-type mosaic eyes (generated using an otherwise wild-type FRT chromosome) also sometimes showed irregular facets, but not the blackened facets or bulbous appearance of itpr mosaic eyes. F, Most dissociated ommatidia from itpr mosaic eyes appeared wild-type–like in appearance, but characteristically many still retained some of the axon terminal (arrow, right), which was almost invariably broken off in preparations from wild-type eyes. G, Ommatidial lengths and whole-cell capacitances in itpr mosaics were similar to those of controls (control = wild-type and itpr/TM6 pooled; mean ± SEM, n = 11–26 ommatidia/cells). Scale bars; (A, B) 80 µm, (C–E) 30 µm, (F) 10 µm.