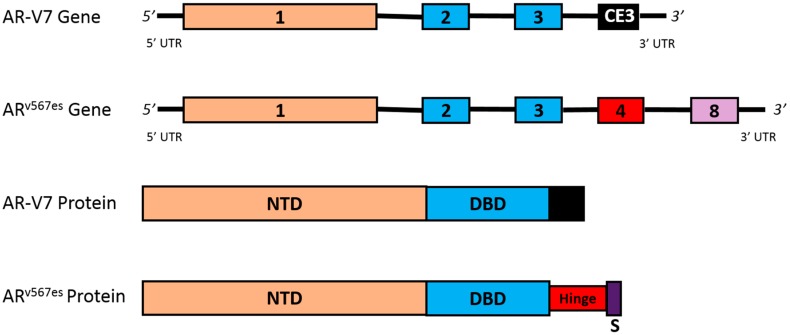
Figure 4.
Clinically-relevant splice variants. This figure depicts the gene and protein structures for the AR-V7 and ARv567es splice variants. Alternate splicing of the AR leads to the formation of the constitutively active, and clinically-relevant, AR-V7 and ARv567es splice variants. AR-V7 is a variant with a cryptic exon 3 instead of exons 4–8. This alternative splicing leads to a protein that has lost the hinge region and LBD. ARv567es is a variant that contains full sequences of exons 1–4, and exon 8; however, exons 5–7 are skipped. As a result of alternative splicing, a frameshift causes the creation of a premature stop codon in exon 8. Both splice variants are constitutively active proteins that can bind to DNA to promote transcription without the need for ligand binding. Abbreviations: ARv567es, androgen receptor splice variant with exons 5–7 skipped; AR-V7, androgen receptor splice variant V7; CE3, cryptic exon 3; NTD, N-terminal transactivation domain; S, premature stop codon; UTR, untranslated region.