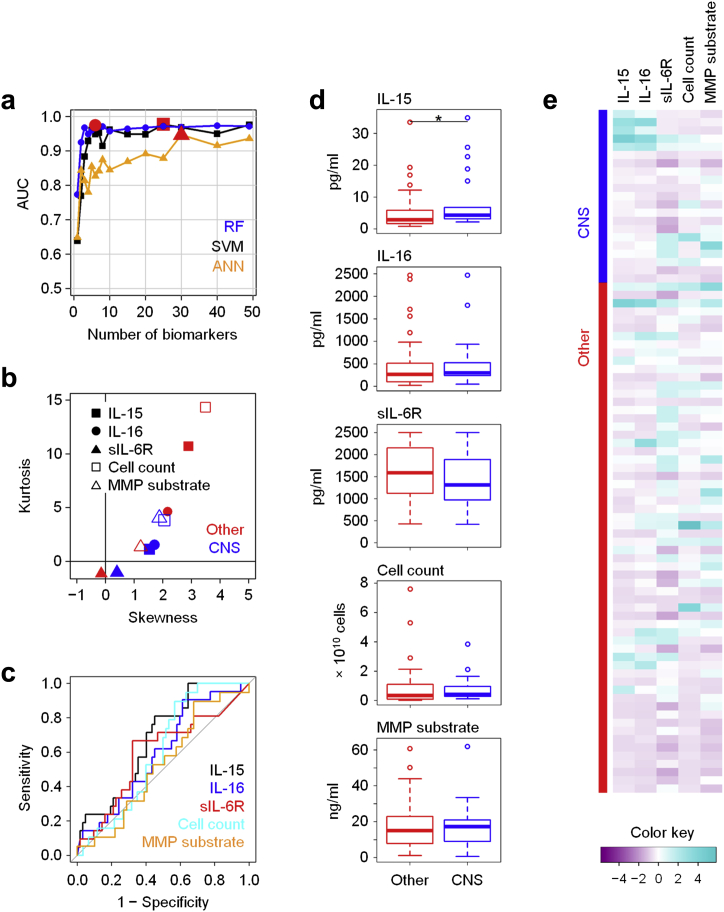
Figure 5.
Local immune fingerprints in coagulase-negative Staphylococcus (CNS) infections. (a) Performance of Random Forest (RF), Support Vector Machine (SVM), and artificial neural network (ANN)–based feature elimination models for the prediction of infections caused by CNS (Staphylococcus epidermidis and related species; N = 21) against all other episodes of peritonitis (N = 62), shown as area under the curve (AUC) depending on the number of biomarkers. Red symbols depict the maximum AUC for each model. (b) Kurtosis and skewness of the top 5 biomarkers selected by RF-based feature elimination. (c) Receiver operating characteristic analysis showing specificity and sensitivity of the top 5 biomarkers. (d) Tukey plots of the top 5 biomarkers in patients with confirmed CNS infections and with all other episodes of peritonitis, as assessed by Mann-Whitney tests (*P < 0.05). (e) Heat map showing the top 5 biomarkers across all patients presenting with acute peritonitis. IL, interleukin; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; sIL-6R, soluble IL-6 receptor.