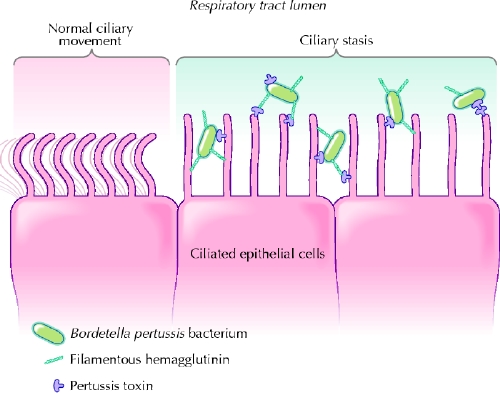
Fig. 1: Synergy between pertussis toxin and filamentous hemagglutinin in binding to ciliated respiratory epithelial cells. Bordetella pertussis attach strongly to the ciliated cells with the combined action of other adhesins (e.g., fimbriae and pertactin). Pertussis toxin has the ability to enter the bloodstream and plays an important role in the induction of clinical immunity. Photo: Lianne Friesen and Nicholas Woolridge
