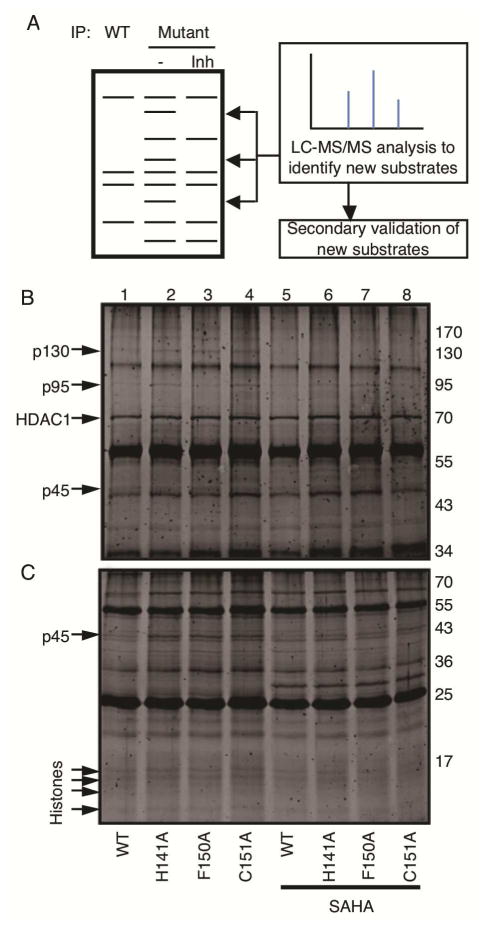
Figure 2.
Substrate trapping by HDAC1 mutants. A) Workflow for the substrate trapping study with initial gel analysis of wild type and mutant HDAC1 immunoprecipitates to identify candidate protein bands. HDAC inhibitor (Inh) was included in a control immunoprecipitate to distinguish associated proteins from substrates by competing for active site binding. Candidate proteins present in only the mutant immunoprecipitate were excised from the gel and identified by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). Substrates were then confirmed using a series of secondary experiments. B/C) Wild type (WT) and mutant HDAC1 (indicated below each lane) were expressed as FLAG-tagged proteins in T-Ag Jurkat cells, immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG agarose, separated by 12% (A) or 16 % (B) SDS-PAGE, and visualized with SyproRuby total protein stain. Arrows indicate immunoprecipitated HDAC1 or possible substrates (p130, p95, p45, or histones) observed in the absence but not presence of competitive active site inhibitor SAHA (0.8 mM).