Figure 7.
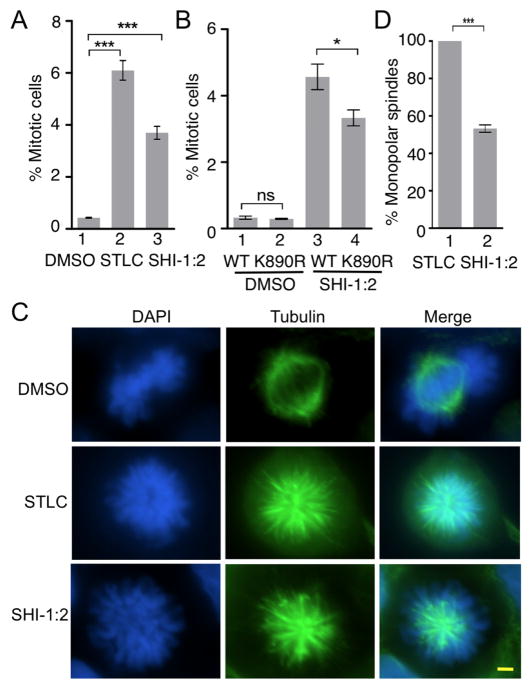
Acetylation of Eg5 contributes to SHI-1:2-induced mitotic arrest. A) HEK293 cells were treated with DMSO, STLC (10 μM) or SHI-1:2 (10 μM) for 48 hr followed by fixing and staining with Alexafluoro®488 conjugated phospho-histone H3 (Ser10) antibody and DAPI. Samples were analyzed by flow cytometry (Figure S16) and percent mitotic cells were plotted. Mean and standard error from three independent trials are shown in Table S4. ***p<0.0001. B) Myc-tagged wild type or K890R mutant Eg5 were transfected into HEK293 cells, treated with SHI-1:2 for 48 hr and subjected to staining with Alexa fluoro®488 conjugated phospho-histone H3 (Ser10) antibody and DAPI prior to flow cytometric analysis. A representative trial is shown in Figure S17. Quantification of the mitotic cells is shown as a histogram. Mean and the standard error from three independent trials are shown in Table S5. *p<0.05. ns – not significant. C) HEK293 cells were treated with DMSO, STLC (10 μM) or SHI-1:2 (10 μM) for 48 hr followed by fixing and staining with α-tubulin (green) and DAPI (blue). Fluorescence microscopy was used to visualize tubulin and DAPI in each cell. Scale bar – 10 μm. D) Quantitative analysis of monopolar spindles present in STLC and SHI-1:2 treated cells from part C. Percentage of monopolar spindles was determined after counting at least 100 mitotic cells. Mean and standard error of four independent trials are shown in Table S6. ***p<0.002.