Table 6. Rat and Cynomolgus Monkey Pharmacokinetics of Compounds 27 and 28a.
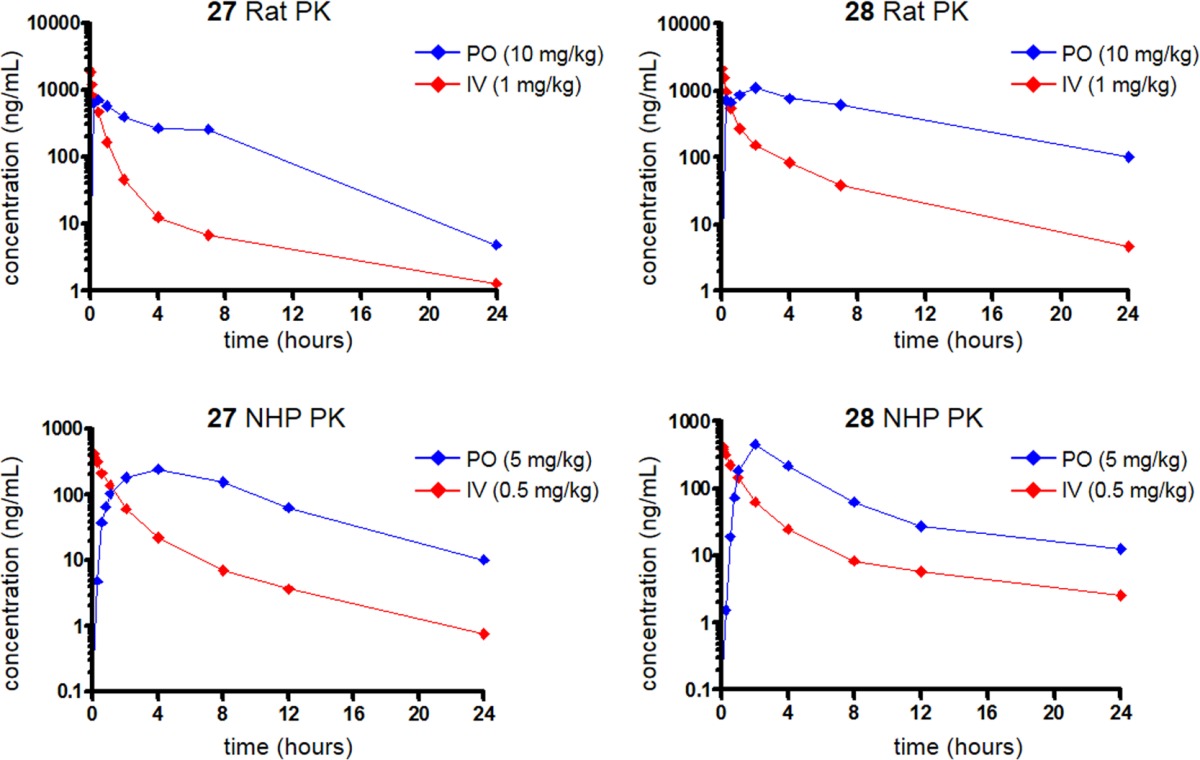
| rat IV
PKb |
rat oral
PKb |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| no. | t1/2 (min)c | MRT (min)c | Clp (mL/min/kg)c | VSS (L/kg)c | Tmax (min)d | Cmax (μM)d | AUC (μM·h)d | % Fd |
| 27 | 390 | 93 | 19.3 | 1.8 | 30 | 4.34 | 14.6 | 53 |
| 28 | 281 | 208 | 9.2 | 1.9 | 90 | 3.33 | 38.0 | 71 |
| cynomolgus
monkey IV PKe |
cynomolgus monkey oral PKe |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| no. | t1/2 (min)c | MRT (min)c | Clp (mL/min/kg)c | VSS (L/kg)c | Tmax (min)d | Cmax (μM)d | AUC (μM·h)d | % Fd |
| 27 | 302 | 163 | 15.5 | 2.5 | 180 | 1.72 | 7.32 | 44 |
| 28 | 563 | 303 | 13.3 | 4.0 | 120 | 1.36 | 6.43 | 35 |
Oral vehicle = 10% polysorbate 80 in 0.5% methyl cellulose; IV vehicle = 10% EtOH, 70% PEG 400, 20% saline.
Average n = 2 male Sprague–Dawley rats.
t1/2 = Terminal phase plasma half-life; MRT = mean residence time; Clp = plasma clearance; VSS = volume of distribution at steady-state.
Tmax = time at which maximum concentration occurs; Cmax = maximum concentration; AUC = area under the curve; F = bioavailability.
Average n = 2 male cynomolgus monkeys.
