Figure 1.
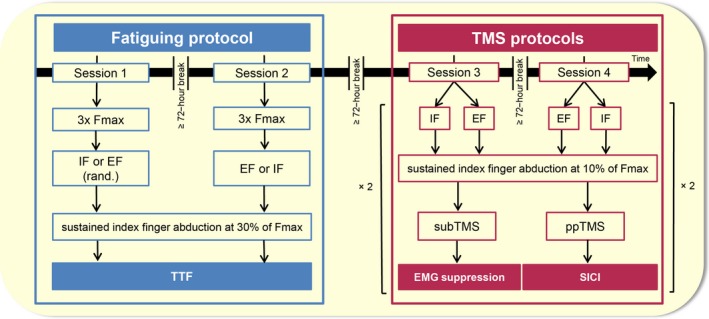
Time course of the four laboratory sessions. The first two sessions (sessions 1 and 2) aimed to outline differences in the time to task failure (TTF) of a submaximal sustained index finger abduction at 30% of F max between an external focus of attention (EF) and an internal focus of attention (IF). In one session, participants were asked to adopt an IF by concentrating on the muscle and finger, while in the other session, they were asked to adopt an EF by concentrating on the goniometer angle. The order of sessions was randomized. Sessions 3 and 4 aimed to compare the activity of M1 during the same two focus of attention conditions by means of subthreshold TMS (subTMS) and paired‐pulse TMS to assess intracortical inhibition; subTMS‐induced electromyographical (EMG) suppression and short‐interval intracortical inhibition (SICI) respectively. The participants performed the same motor task as in sessions 1 and 2 but at only 10% of F max to prevent the effect of fatigue. TMS, transcranial magnetic stimulation.
