Figure 5.
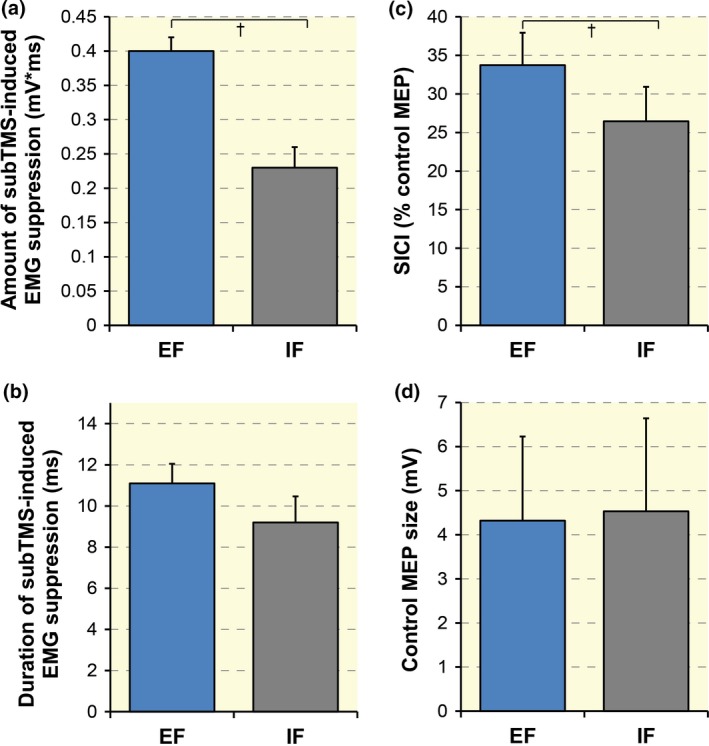
Group data (n = 10) of the amount (a) and the duration (b) of subTMS‐induced electromyographical (EMG) suppression in first dorsal interosseous (FDI) under two focus of attention conditions (EF = 11.1 ± 3.00 ms, IF = 9.2 ± 4.01 ms). The amount of EMG suppression was significantly greater with an external (EF) than with an internal focus of attention (IF). No significant difference was found for the duration. (c) When adopting an EF, the short‐interval intracortical inhibition (SICI) expressed as percentage of control motor‐evoked potential (MEP) in FDI was significantly enhanced contrasted to an IF. (d) Control MEP at 1.2 aMT peak‐to‐peak amplitudes during both attentional conditions. No significant difference was found between the two conditions. † P < 0.01. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean. aMT, active motor threshold; EF, external focus; TMS, transcranial magnetic stimulation.
