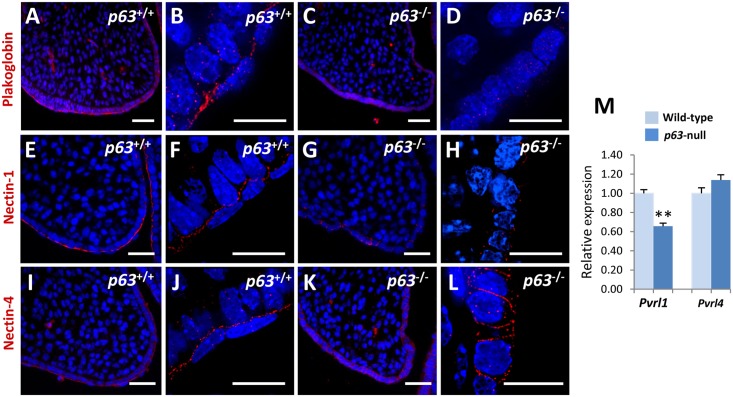
Fig 5. Loss of p63 results in adhesion defects in palatal epithelia.
Immunofluorescence analysis of (A, B) plakoglobin, (E, F) nectin-1, and (I, J) nectin-4 reveals strong expression of these proteins at the junction between the periderm/basal cells in the palatal epithelia of E13.5 wild-type mice. (C, D, G and H) In contrast, plakoglobin and nectin-1 expression are markedly down-regulated in the E13.5 p63-/- palatal epithelia. (K and L) Nectin-4 expression levels in p63-/- palatal shelves are comparable to those of wild-type mice; however deconvolution images reveal that expression of nectin-4, which is normally restricted to the periderm/basal junction, is mis-localized in the epithelia of E13.5 p63-/- palatal shelves and is expressed between adjacent basal cells. (M) qPCR analysis of palatal shelves dissected from E14.0 wild-type and p63-/- mice indicates that Pvrl1 transcripts are significantly reduced in p63-/- palatal shelves while Pvrl4 levels are comparable to wild-type.** = P <0.01, Mann Whitney U test, n = 5 for each genotype. Scale bars: A, C, E, G, I, K, 50 μm; B, D, F, H, J, L, 20 μm.